6 Ways Earth Observations Tackle Real-World Problems
6 Ways Earth Observations Tackle Real-World Problems
This summer, 30 research projects were launched by recent college graduates and early career professionals as part of our DEVELOP program. The aim is to use our satellite observations of Earth to address an environmental or public policy issue. And they have just 10 weeks to do it! On Aug. 10, 2016, the “DEVELOPers” gathered at our Headquarters in Washington, DC to showcase their results. So, how can Earth observations solve real-world problems? Let’s take a look:

1. They help land managers identify the locations of invasive species.
Austin Haney, DEVELOP project co-lead at University of Georgia, has seen first-hand how an invasive species can affect the ecosystem of Lake Thurmond, a large reservoir that straddles the border between Georgia and South Carolina. Birds in the area “behave visibly different,” he said, after they consume a toxic cyanobacteria that lives on Hydrilla verticillata, an invasive aquatic plant. Ingesting the toxin causes a neurodegenerative disease and ultimately death. Scores of birds have been found dead near lake areas where large amounts of the toxin-supporting Hydrilla grow. To help lake managers better address the situation, Haney and project members developed a tool that uses data from the Landsat 8 satellite to map the distribution of Hydrilla across the lake.
Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

2. They help identify wildlife habitat threatened by wildfires.
Maps that depict habitat and fire risk in eastern Idaho previously stopped short of Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve, where shrubs and grasses transition to a sea of ankle-twisting basalt. But the environment is not as inhospitable as it first appears. Throughout the monument there are more than 500 kipukas —pockets of older lava capable of supporting some vegetation. That means it is also prone to burning. Project lead Courtney Ohr explained how her team used data from the Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 satellites to develop a model that can simulate the area’s susceptibility to wildfires. Decision makers can use this model to monitor the remote wildlife habitat from afar.
Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

3. In conjunction with Instagram, they help find seaweed blooms
Who knew that Instagram could be a tool for science? One DEVELOP team searched for photographs of massive seaweed (sargassum) blooms in the Caribbean, mapped the locations, and then checked what satellites could see. In the process, they tested two techniques for finding algae and floating vegetation in the ocean.
Image Credit: Caribbean Oceans Team

4. They help conserve water by reducing urban stormwater runoff.
Atlanta’s sewer system is among the nation’s most expensive. Yet, the city still struggles with stormwater. It’s an uphill climb as new construction paves over more of the city, hindering its ability to absorb rain. The University of Georgia DEVELOP team partnered with The Nature Conservancy to address the problem.
Using satellite imagery, the team was able to pinpoint areas well-poised to capture more of the city’s runoff. They identified 17 communities ripe for expanding green infrastructure and reforestation. The team used the Land-Use Conflict Identification Strategy and Soil and Water Assessment Tool models and Landsat and Terra satellite data. Their analysis provides local groups with a working picture of the city’s water resources.
Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

5. They show the spread of the mite eating away Puerto Rico’s palm trees.
The red palm mite has devastated Puerto Rico’s trees in recent years. The insect chewed its way through coconut palms, bananas, and plantains on the island in the recent decade. Its spread has hurt crops across the Caribbean.
A DEVELOP team led by Sara Lubkin analyzed satellite imagery to track the mites’ rapid spread from 2002. The team mapped changes to vegetation, such as yellowing, and differences in canopy structure. They made use of imagery from Landsat, Hyperion, IKONOS, and aerial views. Their work can be used to mitigate current mite infestations and monitor and prevent future ones.
Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

6. They evaluate landslide-prone areas in the developing world
One team of DEVELOPers took on several projects to aid people in developing nations. This team from Alabama examined satellite imagery to find past landslides in the African nation of Malawi. Factors such as flooding after long periods of drought have made the country increasingly prone to landslides. Blending maps of the landscape, rainfall data, and population centers, the young researchers assessed the areas most at risk—and most in need of education and support—from landslides.
Image Credit: East Africa Disasters II Team
Want to read more about DEVELOP projects, or get involved? Summaries, images, and maps of current and past projects can be viewed HERE. You can also learn how to apply for the DEVELOP program HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
We Found the Universe’s First Type of Molecule

For decades, astronomers searched the cosmos for what is thought to be the first kind of molecule to have formed after the Big Bang. Now, it has finally been found. The molecule is called helium hydride. It’s made of a combination of hydrogen and helium. Astronomers think the molecule appeared more than 13 billion years ago and was the beginning step in the evolution of the universe. Only a few kinds of atoms existed when the universe was very young. Over time, the universe transformed from a primordial soup of simple molecules to the complex place it is today — filled with a seemingly infinite number of planets, stars and galaxies. Using SOFIA, the world’s largest airborne observatory, scientists detected newly formed helium hydride in a planetary nebula 3,000 light-years away. It was the first ever detection of the molecule in the modern universe. Learn more about the discovery:
Helium hydride is created when hydrogen and helium combine.

Since the 1970s, scientists thought planetary nebula NGC 7027—a giant cloud of gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus—had the right environment for helium hydride to exist.

But space telescopes could not pick out its chemical signal from a medley of molecules.

Enter SOFIA, the world’s largest flying observatory!

By pointing the aircraft’s 106-inch telescope at the planetary nebula and using a tool that works like a radio receiver to tune in to the “frequency” of helium hydride, similar to tuning a radio to a favorite station…

…the molecule’s chemical signal came through loud and clear, bringing a decades-long search to a happy end.

The discovery serves as proof that helium hydride can, in fact, exist in space. This confirms a key part of our basic understanding of the chemistry of the early universe. SOFIA is a modified Boeing 747SP aircraft that allows astronomers to study the solar system and beyond in ways that are not possible with ground-based telescopes. Find out more about the mission at www.nasa.gov/SOFIA
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Human Expansion Across Solar System
On this day in 1972, two NASA astronauts landed on the Moon. Now, 45 years later, we have been instructed to return to the lunar surface.
Today at the White House, President Trump signed the Space Policy Directive 1, a change in national space policy that provides for a U.S.-led program with private sector partners for a human return to the Moon, followed by missions to Mars and beyond.

Among other dignitaries on hand for the signing, were NASA astronauts Sen. Harrison “Jack” Schmitt, Buzz Aldrin, Peggy Whitson and Christina Koch.
Schmitt landed on the moon 45 years to the minute that the policy directive was signed as part of our Apollo 17 mission, and is the most recent living person to have set foot on our lunar neighbor.

Above, at the signing ceremony instructing us to send humans back to the lunar surface, Schmitt shows First Daughter Ivanka Trump the Moon sample he collected in 1972.
The effort signed today will more effectively organize government, private industry and international efforts toward returning humans on the Moon, and will lay the foundation that will eventually enable human exploration of Mars.
To learn more, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/new-space-policy-directive-calls-for-human-expansion-across-solar-system
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Tour NASA with One Direction

You might have heard, One Direction filmed their ‘Drag Me Down’ music video at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, and we know you’re dying to take a tour of everything they saw. So, here we go…
1) Space Exploration Vehicle (SEV)

Even though Louis is roving around Johnson Space Center in our Space Exploration Vehicle, its intended destination is quite different. The SEV will be used for in-space missions and for surface explorations of planetary bodies, including near-Earth asteroids and Mars!
2) Robonaut
Harry and Robonaut bonded during their visit to Johnson Space Center for the filming of their music video. This robot will help humans work and explore in space. Working side by side with humans, or going where the risks are too great for people, robots will make it so we never get ‘dragged down’!
3) Partial Gravity Simulator & Space Station Mockup Bike

You can find Niall floating around in our Partial Gravity Simulator, aka POGO, in the new music video. This tool is used to provide accurate simulations of reduced gravity. Astronauts use this for training and to learn how to perform tasks in space.
While Niall floats with POGO, Liam is training on the International Space Station Mockup Bike, aka CEVIS. This bike provides aerobic exercise and is used to countermeasure the harmful effects of exposure to microgravity while on the space station.
4) Orion Spacecraft

The Orion spacecraft will be the first of its kind that will carry humans to deep space and to Mars! It will be the safest, most advanced spacecraft ever built, and Harry, Niall, Louis and Liam all got to check it out.
5) T-38 Jets

Flying these T-38 jet trainers are an important part of preparing to be an astronaut. Flying and landing them acts as a real-life simulation for practicing spacecraft operations. They can even fly at supersonic up to Mach 1.6, and can put their pilots through more than seven Gs!
Much of the western United States began the morning with the view of a super blue blood moon total lunar eclipse. In this silent time lapse video, the complete eclipse is seen over NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, located at the base of the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, California. This Jan. 31 full moon was special for three reasons: it was the third in a series of “supermoons,” when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit -- known as perigee -- and about 14 percent brighter than usual. It was also the second full moon of the month, commonly known as a “blue moon.” The super blue moon will pass through Earth’s shadow to give viewers in the right location a total lunar eclipse. While the Moon is in the Earth’s shadow it will take on a reddish tint, known as a “blood moon.”
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Great Scott, it’s Back to the Future Day – Oct. 21, 2015
What would a time traveler from 1985 discover about NASA today?
It’s Back to the Future Day, the date in the second film that Marty and Doc traveled to in the future. When they arrived in 2015, it looked much different than today’s reality. Although we may not have self-drying jackets or flying cars, we do have some amazing spacecraft and technologies that were not around back when the film was made.

For example, in 1985 we did not have the capability to capture an image like this of our Earth. This full-Earth view captured Monday (10/19/15) by our camera on the Deep Space Climate Observatory, or DSCOVER, was not previously possible. The DSCOVR mission captures a daily sequence of images that show the Earth as it rotates, revealing the whole globe over the course of a day. These images will allow scientists to study daily variations over the entire globe in such features as vegetation, ozone, aerosols and cloud height and reflectivity.
So, we might not be cruising down the street on hover boards, but the movies didn’t get it all wrong in terms of how advanced we’d be in 2015.
When you were a kid, what technologies did you dream we’d have in the future that we may or may not have today? Here’s what two astronauts said:
NASA is much different than it was in 1985. Could we have dreamed these amazing accomplishments that have changed our world and understanding of the universe?
1. “There will be an orbiting laboratory where astronauts from around the world will live and work together.”

When Back to the Future II was set, the International Space Station didn’t exist yet. The first piece of the space station was launched in 1998, and the first crew arrived in 2000. Since November 2000, the station has been continuously occupied by humans.
2. "We will find planets orbiting in the habitable zone of a star, and possibly suited for life."

The first exoplanet, or planet orbiting around a star, was found in 1995. Since then, we’ve discovered around a dozen habitable zone planets in the Earth-size range. While we aren’t able to zoom in to these planets that are light-years away, we’re still closer to finding another Earth-like planet in 2015 than we were in 1985.
3. “Mars will become more populated.”

No, not by humans...yet. But, since the release of Back to the Future II, Mars has become a bit more populated with rovers and orbiters. These scientific spacecraft have played an important role in learning about the Red Planet. We currently have six missions at Mars. With the most recent news of liquid water on the surface of Mars, we can look forward to future missions returning even more data and images. The historical log of all Mars missions, both domestic and international can be found HERE.
4. “We will launch a telescope into orbit that’s capable of looking at locations more than 13.4 billion light years from Earth.”

When Back to the Future II was released, our Hubble Space Telescope had not yet launched into orbit -- something that wouldn’t happen until April 1990. Since then, Hubble has made more than 1.2 million observations, and has traveled more than 3 billion miles along a circular low Earth orbit. For updates on Hubble’s findings, check HERE.
For more information about the technology that we’re developing at NASA, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Time for some Sun salutations 🧘
Flow through 133 days of the Sun's activity from Aug. 12 to Dec. 22, 2022, as captured by our Solar Dynamics Observatory. From its orbit around Earth, SDO has steadily imaged the Sun in 4K resolution for nearly 13 years.
Video description: Mellow music plays as compiled images taken every 108 seconds condenses 133 days of solar observations into an hour-long video. The video shows bright active regions passing across the face of the Sun as it rotates.
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Scott Wiessinger (Lead Producer and editor), Tom Bridgman (Lead Visualizer), Lars Leonhard (music)
6 Ways NASA Technology Makes You Healthier
An important part of our mission is keeping astronauts strong and healthy during stays in space, but did you know that our technology also helps keep you healthy? And the origins of these space innovations aren’t always what you’d expect.
As we release the latest edition of NASA Spinoff, our yearly publication that celebrates all the ways NASA technology benefits us here on Earth, let’s look at some ways NASA is improving wellness for astronauts—and everyone else.
1. Weightless weight-lifting

Without gravity to work against, astronauts lose bone and muscle mass in space. To fight it, they work out regularly. But to get them a good burn, we had to get creative. After all, pumping iron doesn’t do much good when the weights float.
The solution? Elastic resistance. Inventor Paul Francis was already working on a portable home gym that relied on spiral-shaped springs made of an elastic material. He thought the same idea would work on the space station and after additional development and extensive testing, we agreed.
Our Interim Resistive Exercise Device launched in 2000 to help keep astronauts fit. And Francis’ original plan took off too. The technology perfected for NASA is at the heart of the Bowflex Revolution as well as a new line of handheld devices called OYO DoubleFlex, both of which enable an intensive—and extensive—workout, right at home.
2. Polymer coating keeps hearts beating

A key ingredient in a lifesaving treatment for many patients with congestive heart failure is made from a material a NASA researcher stumbled upon while working on a supersonic jet in the 1990s.
Today, a special kind of pacemaker that helps synchronize the left and right sides of the heart utilizes the unique substance known as LaRC-SI. The strong material can be cast extremely thin, which makes it easier to insert in the tightly twisted veins of the heart, and because it insulates so well, the pacemaker’s electric pulses go exactly where they should.
Since it was approved by the FDA in 2009, the device has been implanted hundreds of thousands of times.
3. Sutures strong enough for interplanetary transport

Many people mistakenly think we created Teflon. Not true: DuPont invented the unique polymer in 1938. But an innovative new way to use the material was developed to help us transport samples back from Mars and now aids in stitching up surgery patients.
Our scientists would love to get pristine Martian samples into our labs for more advanced testing. One complicating factor? The red dust makes it hard to get a clean seal on the sample container. That means the sample could get contaminated on its way back to Earth.
The team building the cannister had an idea, but they needed a material with very specific properties to make it work. They decided to use Polytetrafluoroethylene (that’s the scientific name for Teflon), which works really well in space.
The material we commonly recognize as Teflon starts as a powder, and to transform it into a nonstick coating, the powder gets processed a certain way. But process it differently, and you can get all kinds of different results.
For our Mars sample return cannister prototype, the powder was compressed at high pressures into a block, which was then forced through an extruder. (Imagine pressing playdough through a mold). It had never been done before, but the end result was durable, flexible and extremely thin: exactly what we needed.
And since the material can be implanted safely in the human body—it was also perfect as super strong sutures for after surgery.
4. Plant pots that clean the air

It may surprise you, but the most polluted air you breathe is likely the air inside your home and office. That’s especially true these days with energy-efficient insulation: the hot air gets sealed in, but so do any toxins coming off the paint, furniture, cooking gas, etc.
This was a problem NASA began worrying about decades ago, when we started planning for long duration space missions. After all, there’s no environment more insulated than a spaceship flying through the vacuum of space.
On Earth, plants are a big part of the “life support” system cleaning our air, so we wondered if they could do the same indoors or in space.
The results from extensive research surprised us: we learned the most important air scrubbing happens not through a plant’s leaves, but around its roots. And now you can get the cleanest air out of your houseplants by using a special plant pot, available online, developed with that finding in mind: it maximizes air flow through the soil, multiplying the plant’s ability to clean your air.
5. Gas sensor detects pollution from overhead

Although this next innovation wasn’t created with pollution in mind, it’s now helping keep an eye on one of the biggest greenhouse gasses: methane.
We created this tiny methane “sniffer” to help us look for signs of life on Mars. On Earth, the biggest source of methane is actually bacteria, so when one of our telescopes on the ground caught a glimpse of the gas on Mars, we knew we needed to take a closer look.
We sent this new, extremely sensitive sensor on the Curiosity Rover, but we knew it could also be put to good use here on our home planet. We adapted it, and today it gets mounted on drones and cars to quickly and accurately detect gas leaks and methane emissions from pipelines, oil wells and more.
The sensor can also be used to better study emissions from swamps and other natural sources, to better understand and perhaps mitigate their effects on climate change.
6. DNA “paint” highlights cellular damage

There’s been a lot of news lately about DNA editing: can genes be changed safely to make people healthier? Should they be?
As scientists and ethicists tackle these big questions, they need to be sure they know exactly what’s changing in the genome when they use the editing tools that already exist.
Well, thanks to a tool NASA helped create, we can actually highlight any abnormalities in the genetic code with special fluorescent “paint.”
But that’s not all the “paint” can do. We actually created it to better understand any genetic damage our astronauts incurred during their time in space, where radiation levels are far higher than on Earth. Down here, it could help do the same. For example, it can help doctors select the right cancer treatment by identifying the exact mutation in cancer cells.
You can learn more about all these innovations, and dozens more, in the 2019 edition of NASA Spinoff. Read it online or request a limited quantity print copy and we’ll mail it to you!
Earth’s Hot and It’s Cold 🎶(and We Can Tell from Space)
From people and pets to pens and pencils, everything gives off energy in the form of heat. We’ve got special instruments that measure thermal wavelengths, so we can tell whether something is hot, cold or in between. Hotter things emit more thermal energy; colder ones emit less.

We have special instruments in space, zipping around Earth and measuring the hottest and coldest places on our planet.

We can also measure much subtler changes in heat – like when plants cool down as they take up water from the soil and ‘sweat’ it out into the air, in a process called evapotranspiration.

This lets us identify healthy, growing crops around the world.

The instrument that can do all this is called the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2). It just passed a series of rigorous tests at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., proving it’s ready to survive in space.

TIRS-2 is bound for the Landsat 9 satellite, which will continue decades of work studying our planet from space.

Learn more about TIRS-2 and how we see heat from space: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2019/new-landsat-infrared-instrument-ships-from-nasa/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What aspect of spaceflight always blows your mind, even after all this time?
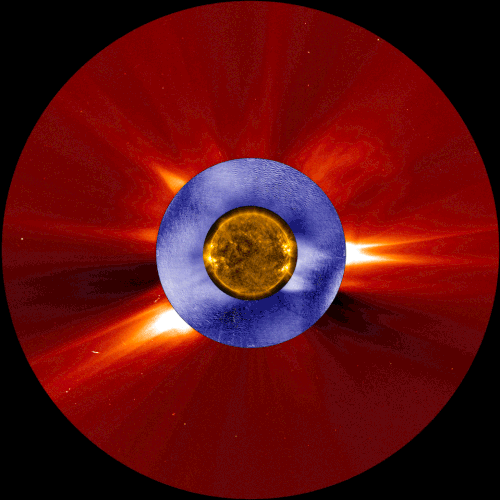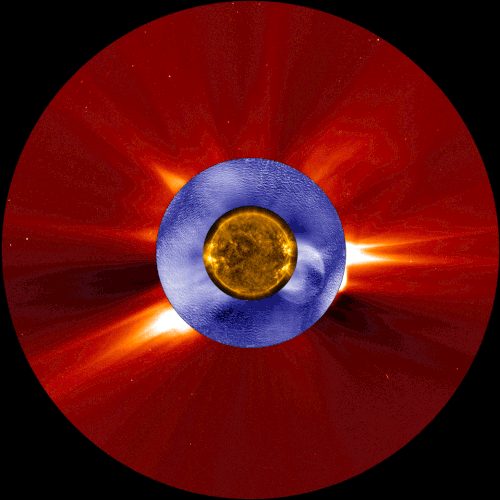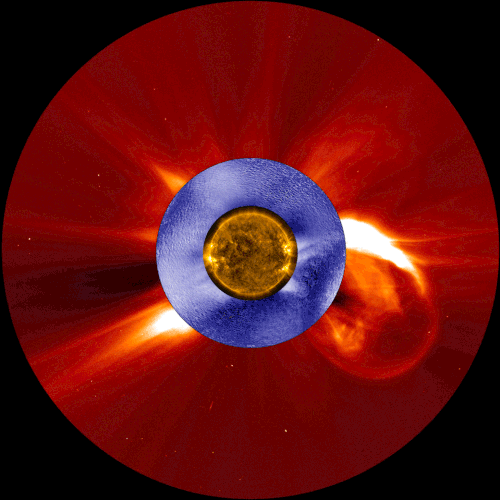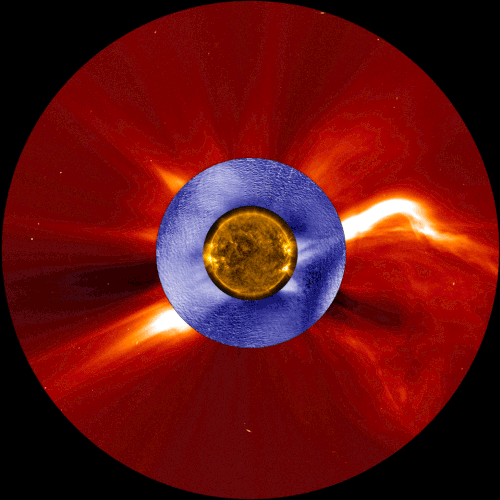
This composite image shows a coronal mass ejection, a type of space weather linked to solar energetic particles, as seen from two space-based solar observatories and one ground-based instrument. The image in gold is from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, the image in blue is from the Manua Loa Solar Observatory’s K-Cor coronagraph, and the image in red is from ESA and NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory.
Our constantly-changing sun sometimes erupts with bursts of light, solar material, or ultra-fast energized particles — collectively, these events contribute to space weather. A new study shows that the warning signs of one type of space weather event can be detected tens of minutes earlier than with current forecasting techniques – critical extra time that could help protect astronauts in space.
Credits: NASA/ESA/SOHO/SDO/Joy Ng and MLSO/K-Cor
-
 thisisacatperson liked this · 4 years ago
thisisacatperson liked this · 4 years ago -
 thnks-fr-th-samulet liked this · 5 years ago
thnks-fr-th-samulet liked this · 5 years ago -
 asiaphotoreview liked this · 7 years ago
asiaphotoreview liked this · 7 years ago -
 enflightdesign liked this · 7 years ago
enflightdesign liked this · 7 years ago -
 best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago
best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mule1971 liked this · 8 years ago
mule1971 liked this · 8 years ago -
 thingsmydadmightlike-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
thingsmydadmightlike-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 carlosemiliopir liked this · 8 years ago
carlosemiliopir liked this · 8 years ago -
 alicerobertstext reblogged this · 8 years ago
alicerobertstext reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 wanderingsigma reblogged this · 8 years ago
wanderingsigma reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 playingjax reblogged this · 8 years ago
playingjax reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 vampirecherrie reblogged this · 8 years ago
vampirecherrie reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 susaniam liked this · 8 years ago
susaniam liked this · 8 years ago -
 jumblejo reblogged this · 8 years ago
jumblejo reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 phoenixbluemusic liked this · 8 years ago
phoenixbluemusic liked this · 8 years ago -
 diabaliful reblogged this · 8 years ago
diabaliful reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ascarosepion reblogged this · 8 years ago
ascarosepion reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 neutrinotempest liked this · 8 years ago
neutrinotempest liked this · 8 years ago -
 poro-oletettu reblogged this · 8 years ago
poro-oletettu reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tombcutie reblogged this · 8 years ago
tombcutie reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mahinthjoe reblogged this · 8 years ago
mahinthjoe reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 artisanscribbles reblogged this · 8 years ago
artisanscribbles reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mossdunce liked this · 8 years ago
mossdunce liked this · 8 years ago -
 aquitainequeen reblogged this · 8 years ago
aquitainequeen reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mercy-angel-09 reblogged this · 8 years ago
mercy-angel-09 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 vi2thesky reblogged this · 8 years ago
vi2thesky reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 1stepforward2stepsbackcarousel reblogged this · 8 years ago
1stepforward2stepsbackcarousel reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 8 years ago
sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rollingfisheyes reblogged this · 8 years ago
rollingfisheyes reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 schpeelah reblogged this · 8 years ago
schpeelah reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 wretchedmeat reblogged this · 8 years ago
wretchedmeat reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 lyanna88-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
lyanna88-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 thegamejustgotmorefierce reblogged this · 8 years ago
thegamejustgotmorefierce reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rlcampos reblogged this · 8 years ago
rlcampos reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 whathappensisalwayshidden liked this · 8 years ago
whathappensisalwayshidden liked this · 8 years ago -
 eskiworks liked this · 8 years ago
eskiworks liked this · 8 years ago -
 wretchedmeat liked this · 8 years ago
wretchedmeat liked this · 8 years ago -
 new-great-age-of-discovery reblogged this · 8 years ago
new-great-age-of-discovery reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 saltheartgal liked this · 8 years ago
saltheartgal liked this · 8 years ago -
 justgo45-blog liked this · 8 years ago
justgo45-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 omgpickaname reblogged this · 8 years ago
omgpickaname reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 omgpickaname liked this · 8 years ago
omgpickaname liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts