“Mom, Pls”

“Mom, pls”
More Posts from Space-and-stuff-blog1 and Others

Blick vom Rande des Tiefenbacher Moos auf die Hörnerkette - Berge (Ofterschwanger Horn, Sigiswanger Horn, Rangiswanger Horn). Allgäu, Bayern.
By Thorsten Nunnemann
Portfolio | Facebook | Twitter

This gigantic lens, built for NASA to record space launches, is up for sale: http://bokeh.digitalrev.com/article/gigantic-1000mm-nasa-lens-up-for-sale




Anticrepuscular rays are spectacular optical phenomena that are quite rare and they require the viewer to have his or her back to the sun or sunset point. They are columns of sunlit air streaming through gaps in clouds. Yet while the former seem to converge from the sun, anticrepuscular rays converge toward the antisolar point, the point in the sky directly opposite the sun, creating some stunning effects. (Source)
Largest Collection of Planets EVER Discovered!
Guess what!? Our Kepler mission has verified 1,284 new planets, which is the single largest finding of planets to date. This gives us hope that somewhere out there, around a star much like ours, we can possibly one day discover another Earth-like planet.

But what exactly does that mean? These planets were previously seen by our spacecraft, but have now been verified. Kepler’s candidates require verification to determine if they are actual planets, and not another object, such as a small star, mimicking a planet. This announcement more than doubles the number of verified planets from Kepler.

Since the discovery of the first planets outside our solar system more than two decades ago, researchers have resorted to a laborious, one-by-one process of verifying suspected planets. These follow-up observations are often time and resource intensive. This latest announcement, however, is based on a statistical analysis method that can be applied to many planet candidates simultaneously.
They employed a technique to assign each Kepler candidate a planet-hood probability percentage – the first such automated computation on this scale, as previous statistical techniques focused only on sub-groups within the greater list of planet candidates identified by Kepler.
What that means in English: Planet candidates can be thought of like bread crumbs. If you drop a few large crumbs on the floor, you can pick them up one by one. But, if you spill a whole bag of tiny crumbs, you’re going to need a broom. This statistical analysis is our broom.

The Basics: Our Kepler space telescope measures the brightness of stars. The data will look like an EKG showing the heart beat. Whenever a planet passes in front of its parent star a viewed from the spacecraft, a tiny pulse or beat is produced. From the repeated beats, we can detect and verify the existence of Earth-size planets and learn about their orbits and sizes. This planet-hunting technique is also known as the Transit Method.

The number of planets by size for all known exoplanets, planets that orbit a sun-like star, can be seen in the above graph. The blue bars represent all previously verified exoplanets by size, while the orange bars represent Kepler’s 1,284 newly validated planets announced on May 10.

While our original Kepler mission has concluded, we have more than 4 years of science collected that produced a remarkable data set that will be used by scientists for decades. The spacecraft itself has been re-purposed for a new mission, called K2 – an extended version of the original Kepler mission to new parts of the sky and new fields of study.

The above visual shows all the missions we’re currently using, and plan to use, in order to continue searching for signs of life beyond Earth.
Following Kepler, we will be launching future missions to continue planet-hunting , such as the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), and the James Webb Space Telescope. We hope to continue searching for other worlds out there and maybe even signs of life-as-we-know-it beyond Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

In this new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, a firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy LEDA 36252 — also known as Kiso 5649.
(via LEDA 36252, a cosmic tadpole | ESA/Hubble)

The Great Red Spot on Jupiter gets smaller by 580 miles per year



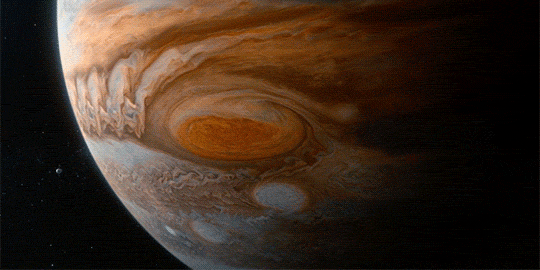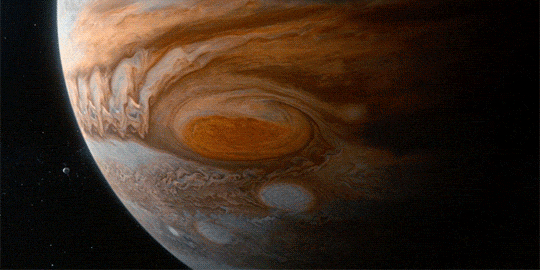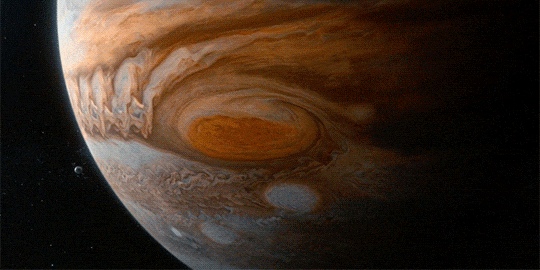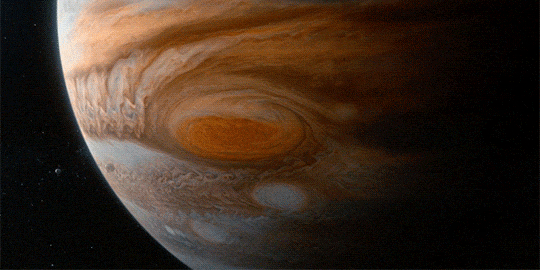






“To make this journey, we’ll need imagination, but imagination alone is not enough, because the reality of nature is far more wondrous than anything we can imagine.”
These are just a few of the beautiful visual effects from Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey
-
 vincentj1271 liked this · 3 months ago
vincentj1271 liked this · 3 months ago -
 poynter66 liked this · 10 months ago
poynter66 liked this · 10 months ago -
 migvintof liked this · 1 year ago
migvintof liked this · 1 year ago -
 picknesajus liked this · 1 year ago
picknesajus liked this · 1 year ago -
 for-the-collection liked this · 2 years ago
for-the-collection liked this · 2 years ago -
 maleauctionblock liked this · 2 years ago
maleauctionblock liked this · 2 years ago -
 bilexualclarke liked this · 2 years ago
bilexualclarke liked this · 2 years ago -
 kings-of-the-highlands reblogged this · 4 years ago
kings-of-the-highlands reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wizardwinterwolf liked this · 4 years ago
wizardwinterwolf liked this · 4 years ago -
 crystalline-kaleidoscope reblogged this · 5 years ago
crystalline-kaleidoscope reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 honhonbonbon liked this · 5 years ago
honhonbonbon liked this · 5 years ago -
 styluhss reblogged this · 5 years ago
styluhss reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lost-faith liked this · 5 years ago
lost-faith liked this · 5 years ago -
 mloveslouis28 liked this · 5 years ago
mloveslouis28 liked this · 5 years ago -
 greengrassandcyansea liked this · 5 years ago
greengrassandcyansea liked this · 5 years ago -
 weareonejazzhand liked this · 5 years ago
weareonejazzhand liked this · 5 years ago -
 lyricailove reblogged this · 5 years ago
lyricailove reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 snore-gasmm reblogged this · 5 years ago
snore-gasmm reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 batmanxoxo reblogged this · 5 years ago
batmanxoxo reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 batmanxoxo liked this · 5 years ago
batmanxoxo liked this · 5 years ago -
 aheartandashirt reblogged this · 5 years ago
aheartandashirt reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sexatoxbridge reblogged this · 5 years ago
sexatoxbridge reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mjmuse liked this · 5 years ago
mjmuse liked this · 5 years ago -
 tacosalv5 liked this · 5 years ago
tacosalv5 liked this · 5 years ago -
 mymouthisfullofrosepetals reblogged this · 5 years ago
mymouthisfullofrosepetals reblogged this · 5 years ago
Just Space, math/science and nature. Sometimes other things unrelated may pop up.
119 posts




