19 Most Common Character Flaws In Horror Fiction
19 Most Common Character Flaws in Horror Fiction
Curiosity: Characters who are overly curious may investigate dangerous situations or places, leading to their downfall.
Arrogance: Arrogant characters may underestimate threats or refuse to heed warnings, putting themselves in danger.
Recklessness: Characters who act impulsively or without considering the consequences may find themselves in perilous situations.
Naivety: Naive characters may be easily deceived or manipulated by villains or supernatural forces.
Overconfidence: Overconfident characters may believe they can handle any situation, leading them to take unnecessary risks.
Stubbornness: Stubborn characters may refuse to listen to advice or change their course of action, even when it's clear they're in danger.
Greed: Greedy characters may prioritize personal gain over safety, leading them to make unethical or dangerous choices.
Distrust: Characters who are overly distrustful may alienate allies or miss crucial information, making them more vulnerable.
Cowardice: Cowardly characters may abandon others in dangerous situations or fail to confront threats when necessary.
Impulsiveness: Impulsive characters may act without thinking, leading to mistakes or putting themselves in harm's way.
Lack of Empathy: Characters who lack empathy may disregard the well-being of others, making them more susceptible to manipulation or isolation.
Overprotectiveness: Overprotective characters may prioritize the safety of loved ones to the detriment of their own safety or the safety of others.
Addiction: Characters who are addicted to substances or behaviors may make irrational decisions or be more easily controlled by external forces.
Obsession: Characters who are obsessed with a goal or idea may pursue it at any cost, even endangering themselves or others.
Paranoia: Paranoid characters may see threats where none exist, leading them to take extreme measures or isolate themselves unnecessarily.
Lack of Self-awareness: Characters who lack self-awareness may fail to recognize their own limitations or the impact of their actions on others.
Insecurity: Insecure characters may doubt their own abilities or judgment, making them more susceptible to manipulation or self-destructive behavior.
Ignorance: Characters who are ignorant of the true nature of the threats around them may underestimate their danger or fail to take necessary precautions.
Desperation: Characters who are desperate may make rash decisions or ally themselves with dangerous individuals or entities in hopes of achieving their goals.
More Posts from Watergeus and Others
ᴡʀɪᴛɪɴɢ ʙᴏᴅʏ ʟᴀɴɢᴜᴀɢᴇ
Anger
Anger is one expression of fight-or-flight mode — an automatic, instinctive reaction to a threat. In many cases, there is an underlying fear of being harmed. Thanks to autonomic nervous system arousal, the heart rate increases, pupils dilate, and the face may flush. Other signs of anger
Balling the fists
Crossing the arms tightly
Clenching the fists once arms are crossed
Tight-lipped smile
Clenched teeth
Shaking a finger like a club
Stabbing a finger at someone
Attraction
Pupils dilate
Women will cross and uncross legs to draw attention to them
Mirroring – (usually unconsciously) mimicking the other person’s body language
Closed to Conversation
Keeping the hands in the pockets (esp. men)
Arms and legs crossed
Sitting back
Folding the hands together on a table (creates a barrier)
The “figure-four” leg cross (setting the ankle of one leg on the knee of the other) and then grabbing the lower half of the top leg with both hands.
Openness and Honesty
Exposure of the palms
Arms and legs unfolded
Leaning forward
Submissive Signals
Smiling – that’s why some people smile when they’re upset or afraid
Slumping the shoulders
Doing anything to appear smaller
Distress
Men in particular have a tendency to stroke or rub the nape of the neck when they’re upset. It acts as a self-soothing gesture to deal with a “pain in the neck.”
Crossed arms – arms act like a protective barrier
Self-hugging – arms are crossed, hands gripping upper arms
One-arm cross – one arm crosses the body to hold or touch the other arm – women keep a hand on a purse or bag strap to make this look more natural
Clutching a purse, briefcase, or bag with both arms
Adjusting cuffs or cuff-links (men’s version of the purse-strap grab)
Folding the hands together in front of the crotch (men)
Lying
Lying causes a subtle tingling in the face and neck, so the gestures below are attempts to eliminate that feeling
Covering the mouth – can be like a shh gesture, or they may cover the mouth completely – some people try to cover it by coughing
Touching or rubbing the nose or just below the nose – often a quick, small gesture, not a scratch
Rubbing the eyes (especially men)
Scratching the neck with the index finger
Superiority, Confidence, Power, Dominance
Steepling the fingers (aka setting the tips of the fingers together)
Folding the hands behind the back
Thumbs sticking out from pockets when hands are in pockets (can be front or back pockets)
Hands on hips
Straddling a chair
Hands folded behind the head while sitting up (in men)
[source]
Honestly? My main piece of advice for writing well-rounded characters is to make them a little bit lame. No real living person is 100% cool and suave 100% of the time. Everyone's a little awkward sometimes, or gets too excited about something goofy, or has a silly fear, or laughs about stupid things. Being a bit of a loser is an incurable part of the human condition. Utilize that in your writing.
20 secrets that your character has
1. Hidden Identity: The character is living under an assumed name and concealing their true identity for personal or safety reasons.
2. Past Trauma: The character has experienced a significant traumatic event in their past that they have kept secret, shaping their behavior and motivations.
3. Forbidden Love: The character is involved in a romantic relationship that goes against societal norms or has complications, forcing them to keep it hidden.
4. Hidden Talent: The character possesses a remarkable talent or skill that they have kept hidden from others, fearing judgment or exploitation.
5. Criminal Past: The character has a history of involvement in criminal activities, either as a former offender or as an undercover agent, which they keep concealed from their current life.
6. Family Secret: The character comes from a family with a dark or scandalous secret that they are determined to keep hidden, even if it means sacrificing their own happiness.
7. Betrayal: The character has betrayed someone close to them in the past, and they carry the guilt and shame of their actions as a closely guarded secret.
8. Hidden Agenda: The character is harboring a hidden agenda or ulterior motive, manipulating events and people to serve their own interests.
9. Hidden Wealth: The character possesses significant wealth or resources that they keep hidden to maintain a humble or low-profile existence.
10. Supernatural Abilities: The character possesses supernatural abilities, such as telekinesis or mind-reading, which they keep concealed for fear of persecution or exploitation.
11. Lost Memories: The character has gaps in their memory or a forgotten past that they are desperate to uncover, unsure of what they might discover.
12. Hidden Agenda: The character is working undercover or as a double agent, keeping their true intentions and loyalties hidden from those around them.
13. Terminal Illness: The character has been diagnosed with a serious illness but chooses to keep it a secret, not wanting to burden others or alter their relationships.
14. Stolen Identity: The character has assumed someone else's identity, perhaps due to a troubled past or to escape a dangerous situation.
15. Secret Society: The character is a member of a secretive organization or society with its own rules, rituals, and agenda, which they keep hidden from the outside world.
16. Guilty Pleasure: The character has a guilty pleasure or indulges in a secret hobby that is incongruent with their public image or perceived personality.
17. Hidden Fear: The character has a deep-rooted fear or phobia that they go to great lengths to hide from others, fearing it will make them appear weak or vulnerable.
18. Lost Love: The character had a past love or relationship that ended tragically or abruptly, and they keep their feelings and memories associated with it concealed from others.
19. Hidden Enemy: The character is secretly being targeted or pursued by an unknown enemy or antagonist, and they must keep their guard up to protect themselves and those around them.
20. Unfulfilled Dreams: The character harbors dreams and aspirations that they have never shared with anyone, feeling uncertain or afraid of pursuing them.
Follow me on my IG for more Content. https://instagram.com/saraswritingtipps?igshid=NTc4MTIwNjQ2YQ==
Can you please share some words to use instead of "Look", I really struggle with that, it's always "She looked at him in shock" or "He looked at her with a smile". I know there's "Gazed" and "Glanced" but I wanted some advice to use "Look" less
Words To Use Instead of "Look"
Words Closest in Meaning (w diff connotations!):
stare
eye
study
behold
glimpse
peek
glance
notice
observe
inspect
regarding
view
review
look-see
get an eyeful
peer
give the eye
eyeball
size up
size up
check out
examine
contemplate
scan
recognize
sweep
once-over
judge
watch
glare
consider
spot
scrunitize
gaze
gander
ogle
yawp
Other (more fancy) words:
glimmer
sntach
zero in
take stock of
poke into
mope
glaze
grope
rummage
frisk
probe
rivet
distinguish
witness
explore
gloat
scowl
have a gander
comb
detect
surveillance
squint
keeping watch
rubberneck
pout
bore
slant
ignore
audit
pipe
search
note
speculation
simper
FIVE TIPS FOR WRITING BETTER ROLEPLAY REPLIES struggling to get interactions? try incorporating these tips into your replies!
use the five senses. sight, smell, touch, hearing, taste. where are your muses currently standing? what does the air smell like? are there birds chirping or people walking by? is there a battle in the distance? does the wooden floor beneath them creak when they walk? is the other muse wearing cologne or perfume? describe the world around them in vivid detail and paint a picture of their environment. this will help your writing partner envision the space.
don't keep everything internal. your muse's internal commentary is important, of course, but when an entire reply is only their inner thoughts, it doesn't give your writing partner anything to go on (unless their character can read minds). make sure you add action, story progression, or character movement in a reply, or provide enough dialogue for the other muse to respond to.
end your reply with a question. at the very end of your reply, have your muse ask the other character a question, or pepper a few questions throughout the reply. this gives the other writer a perfect jumping off point for their response.
incorporate npcs and other things happening nearby. maybe your muses are in a library, and the librarian won't stop shushing them. maybe your muse gets a call from their best friend in the middle of the conversation with horrible news. maybe your muses are in a hotel room, and they hear a noisy party in the room next door. your muses aren't the only two people in the universe - expand upon it with details and breathe further life into this world. it makes things so much more fun.
don't forget the other muse. i think we all struggle with this one the most. we get so caught up describing our own muse and their own thoughts and actions that we forget they're interacting with someone else. try describing the other character's stance or facial expression, the way they cross their arms. maybe their makeup is really beautiful. maybe their hair is nice. maybe they smell really bad. maybe the last time your muses interacted, they had a big fight. don't take up your entire reply talking about your muse only; talk about the other character. give the other writer something to smile about and comment on - "i loved what your muse noticed about mine! i loved their observations! they were so right!" make the other writer feel seen. this is a great way to show them you're reading their replies, loving their writing, and noticing little details about their muse.
Writing Body Language
How to Improve your writing
This is something that happens every day in your life. A shift of your eyebrow in skepticism, or the way your lip may twitch to a half smile cause you’re trying not to laugh. These behaviors are vital for writing in character, because not only do the allow you to visually see what is happening but it is also reaffirming whatever emotion your character is showing.
So why should you write it?
Much of human communication is non-verbal which means you need to also translate this non-verbal reaction in a post. It allows you to greatly enhance the emotions of another character and always another person to ‘visually’ see how they feel in a post. Most of all, this will add depth and volume to your post to make it feel more real. IT will make your character feel like a human instead of just another fictional person you look at from above.
Below you will find a list different type of emotions and what sort of body language can be exhibited to them.
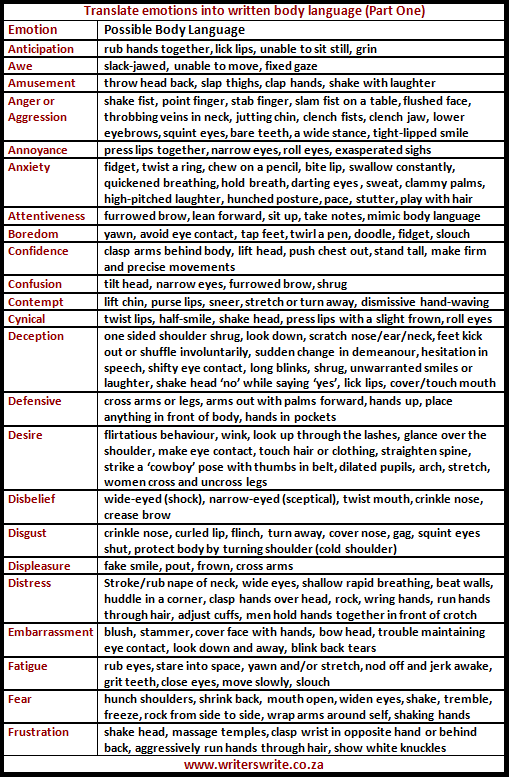
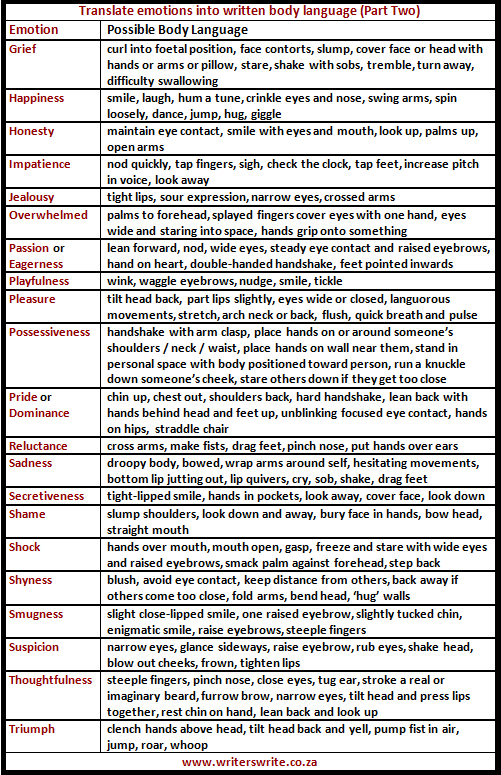
Three ways to accent an action.
When writing about emotions, there are different ways to verbally write them out. Each one is unique in their own way, allowing you to show more about the emotion.
Emphasize the Emotion. But doing this, you are expressing both the emotion and the body language. We’ll use a simple example. It’s short and simple yet you can sense he is happy. John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall.
Complicate the Emotion. Sometimes, even when you are feeling one emotion, deep down rooted underneath the facade of it all, there is actually an underlining emotion they feel. This is something you have to truly express otherwise no one will know. John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall. However, it was obvious by the way his nose crinkled that he was disgusted by the actions beforehand. Instead, John covered it up by appearing pleased today.
Contradict the Emotion. This is a little different than complicate. Contradicting means that you are claiming one thing when in fact its the other. In many ways, this has a variety of uses, from inner depth of the truth to what you see in person, or someone creating a wall. It could be considered a lie, but when is anything that easy? John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall. In truth, once he was in the classroom, his shoulders slumped and a pout crossed his lips when no one was around, showing just how displeased he was with the situation.
Remember that you do not always have to contradict or complicate anything. Sometimes all you need to do is emphasize and that will be just fine. You don’t always have to have an underlining complicated for an emotion to make it more enhanced.
Do be afraid to use the Thesaurus to also improve an emotion. Such things as “happy” is a nice emotional word, but think of how much more powerful it is when you heard some is “overjoyed” or “content.” She how these emotions matched up with a body language can give two different styles of happiness? Mix and match to find what works best for your character at the time.
More In Depth Information
What I’ve stated above is more of a simplistic overview. IF you truly want to improve yourself, go to this
LINK HERE
To see just how much body language can reveal about a person. You will find things such as how a person lies, how the eyes reaction, the positioning of a person in personal space, mouth, and head body language and so much more.
Use these resources to greatly increase the reactions of your character to another and create a more life-like world.
Oh my gosh. I just found this website that walks you though creating a believable society. It breaks each facet down into individual questions and makes it so simple! It seems really helpful for worldbuilding!
hey writers! OneLook Thesaurus lets you find that word you can’t think of but can describe! go check it out!



10 Tips for Crafting Authentic Characters
Give them depth: Create characters with multidimensional personalities, including strengths, weaknesses, quirks, and flaws. They should have a mix of virtues and vices that make them relatable and interesting.
Provide backstory: Develop a detailed backstory for each character, even if only a fraction of it makes it into your story. Understanding a character's past experiences, traumas, and motivations will inform their actions and decisions in the present.
Show their emotions: Allow your characters to express a range of emotions realistically. Show how they react to different situations, both internally and externally, to make them feel human and relatable.
Give them distinct voices: Each character should have a unique way of speaking, with distinct vocabulary, syntax, and speech patterns. This helps readers differentiate between characters and adds authenticity to their dialogue.
Create internal conflicts: Give your characters inner struggles and conflicting desires that they must grapple with throughout the story. Internal conflicts add depth and complexity to characters, making them more believable.
Show their relationships: Develop meaningful relationships between characters, whether they're familial, romantic, platonic, or adversarial. Show how these relationships evolve and influence the characters' development over time.
Make them evolve: Characters should grow and change over the course of the story, driven by their experiences and the challenges they face. Allow them to learn from their mistakes, overcome obstacles, and develop as individuals.
Ground them in reality: Anchor your characters in the real world by giving them relatable experiences, hobbies, jobs, or cultural backgrounds. Incorporating realistic details adds depth and authenticity to their portrayal.
Show their flaws: Imperfect characters are often the most compelling. Don't be afraid to showcase your characters' flaws and vulnerabilities; these imperfections make them more relatable and human.
Give them agency: Allow your characters to drive the plot forward through their actions, decisions, and choices. Avoid making them passive observers or mere vehicles for the story's events. Characters with agency feel more authentic and engaging to readers.
-
 niahadithi liked this · 1 month ago
niahadithi liked this · 1 month ago -
 ashl0390 liked this · 1 month ago
ashl0390 liked this · 1 month ago -
 mallualu liked this · 2 months ago
mallualu liked this · 2 months ago -
 the-dancing-and-the-dreaming reblogged this · 3 months ago
the-dancing-and-the-dreaming reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 wynters-writings liked this · 3 months ago
wynters-writings liked this · 3 months ago -
 unicornwithachainsaw83 liked this · 4 months ago
unicornwithachainsaw83 liked this · 4 months ago -
 pandorasboxofworlds reblogged this · 4 months ago
pandorasboxofworlds reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 vivienneperseus liked this · 4 months ago
vivienneperseus liked this · 4 months ago -
 boohoo-d0lls reblogged this · 4 months ago
boohoo-d0lls reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 roboticskulls liked this · 4 months ago
roboticskulls liked this · 4 months ago -
 roselyn-writing reblogged this · 4 months ago
roselyn-writing reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 burneraccsblog liked this · 4 months ago
burneraccsblog liked this · 4 months ago -
 transparententhusiastmentality liked this · 5 months ago
transparententhusiastmentality liked this · 5 months ago -
 vibrantcoloursinmyhead liked this · 5 months ago
vibrantcoloursinmyhead liked this · 5 months ago -
 lolamultifandom reblogged this · 5 months ago
lolamultifandom reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 minecraftcreepercat liked this · 5 months ago
minecraftcreepercat liked this · 5 months ago -
 voidozooid liked this · 6 months ago
voidozooid liked this · 6 months ago -
 taking-whatsnotyours reblogged this · 6 months ago
taking-whatsnotyours reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 barrelkidd liked this · 6 months ago
barrelkidd liked this · 6 months ago -
 our-lady-of-venom liked this · 6 months ago
our-lady-of-venom liked this · 6 months ago -
 jerrgirl003 liked this · 6 months ago
jerrgirl003 liked this · 6 months ago -
 franticjumpingbean liked this · 6 months ago
franticjumpingbean liked this · 6 months ago -
 fantasmadaagnes liked this · 6 months ago
fantasmadaagnes liked this · 6 months ago -
 wellandsky liked this · 7 months ago
wellandsky liked this · 7 months ago -
 t-rottengod liked this · 7 months ago
t-rottengod liked this · 7 months ago -
 bearrycool liked this · 7 months ago
bearrycool liked this · 7 months ago -
 yellopinkjello liked this · 7 months ago
yellopinkjello liked this · 7 months ago -
 eleazar2313019 liked this · 7 months ago
eleazar2313019 liked this · 7 months ago -
 wowdragonhead liked this · 7 months ago
wowdragonhead liked this · 7 months ago -
 lavenderdisdain liked this · 7 months ago
lavenderdisdain liked this · 7 months ago -
 yulianie liked this · 7 months ago
yulianie liked this · 7 months ago -
 keeperofsecretsunderthehill liked this · 7 months ago
keeperofsecretsunderthehill liked this · 7 months ago -
 nikopie liked this · 7 months ago
nikopie liked this · 7 months ago -
 rauhallinen-hauki liked this · 7 months ago
rauhallinen-hauki liked this · 7 months ago -
 thisfeelslike-iykyk liked this · 7 months ago
thisfeelslike-iykyk liked this · 7 months ago -
 intergalactixprincx liked this · 8 months ago
intergalactixprincx liked this · 8 months ago -
 uni120 liked this · 8 months ago
uni120 liked this · 8 months ago -
 thetwistedarchives liked this · 8 months ago
thetwistedarchives liked this · 8 months ago -
 cookiesjar95 reblogged this · 8 months ago
cookiesjar95 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 kaitolupin liked this · 8 months ago
kaitolupin liked this · 8 months ago -
 amazingicecoldloser liked this · 8 months ago
amazingicecoldloser liked this · 8 months ago -
 socklostinthewasher liked this · 8 months ago
socklostinthewasher liked this · 8 months ago -
 vanillamidnight-us reblogged this · 8 months ago
vanillamidnight-us reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 wonderlustxennial liked this · 8 months ago
wonderlustxennial liked this · 8 months ago -
 bheska liked this · 8 months ago
bheska liked this · 8 months ago -
 auntopossum liked this · 9 months ago
auntopossum liked this · 9 months ago -
 deepsaladcollective reblogged this · 9 months ago
deepsaladcollective reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 thelastbarricade liked this · 9 months ago
thelastbarricade liked this · 9 months ago

