Follow Your Passion: A Seamless Tumblr Journey
Medical University - Blog Posts
The Physiology Of The Liver

The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous functions including metabolism, immunity, digestion, detoxification, and vitamin storage. It weighs around 2% of an adult’s body weight and is unique due to its dual blood supply from the portal vein (75%) and the hepatic artery (25%).
Cellular Structure
The liver’s functional unit is the lobule, which is hexagonal in shape. Each corner of the hexagon has a portal triad consisting of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. The lobule is composed mainly of hepatocytes, which have distinct apical and basolateral membranes. Hepatocytes are categorized into three zones based on their function and blood supply:
Zone I (periportal region): Closest to the blood supply, involved in oxidative metabolism (e.g., gluconeogenesis, bile formation).
Zone II (pericentral region): Sits between Zones I and III.
Zone III: Farthest from the blood supply, primarily involved in detoxification and biotransformation.
Blood and bile flow in opposite directions within the liver. The space of Disse, between the hepatocytes and the sinusoidal lumen, contains Kupffer cells (macrophages) and Ito cells (fat-storing stellate cells).
Development
The liver develops from endodermal cells of the foregut as the hepatic diverticulum around the fourth week of embryonic development. It undergoes complex differentiation influenced by various pathways (e.g., Wnt/β-catenin, FGF). By the sixth week, the liver participates in hematopoiesis, and hepatocytes begin bile production by the 12th week.
Organ Systems and Functions
The liver interacts with multiple body systems:
Digestive and Metabolic Roles: Aids in digestion, stores fat-soluble vitamins, and handles cholesterol.
Hematological Functions: Produces clotting factors and proteins.
Detoxification: Metabolizes drugs and other xenobiotics through phase I (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) and phase II (conjugation) reactions.
Bilirubin Metabolism: Converts heme to unconjugated bilirubin, then conjugates it for excretion.
Hormonal and Protein Synthesis: Involved in thyroid hormone activation and synthesis of nearly all plasma proteins.
Related Testing
Liver function tests (LFTs), including ALT, AST, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), help assess liver health. Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI are also employed to identify liver abnormalities.
Pathophysiology
Cirrhosis results from chronic liver injury (e.g., due to alcoholism, hepatitis B and C), leading to fibrosis and necrosis. It causes symptoms like portal hypertension, coagulopathy, and jaundice. Hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E), autoimmune diseases (e.g., primary biliary cholangitis), and metabolic conditions (e.g., non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) also contribute to liver pathology.
Clinical Significance
Understanding liver physiology helps manage conditions like viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, benign liver lesions, and liver cancers. Early detection through appropriate testing and management strategies is essential for preventing end-stage liver disease and improving patient outcomes
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
Confused by ontology & epistemology? A short guide to help you navigate this aspect of research design

Introduction
For many graduate students pursuing advanced degrees like PhDs or Master’s, the realm of philosophical paradigms, ontology, and epistemology often appears daunting and abstract. Terms like positivism, constructivism, and critical realism can seem overwhelming, especially when these concepts play a fundamental role in shaping research methodologies and approaches. This guide aims to demystify these concepts step by step, providing clarity on their definitions, significance, and implications for academic research.
Understanding Ontology and Epistemology

At the heart of research design lie two foundational concepts: ontology and epistemology. Ontology concerns itself with the nature of reality — what exists and how it exists. It indulges into questions about the fundamental nature of the world, whether objective reality exists independently of human perception, or if reality is constructed through subjective experiences. Epistemology, on the other hand, investigates the nature of knowledge — how knowledge is acquired, validated, and understood. It explores the ways researchers come to know and understand phenomena, addressing questions about the validity of different sources of knowledge and the role of perception and interpretation in knowledge production.
The Role of Philosophical Paradigms
Philosophical paradigms provide overarching frameworks that guide researchers in defining their ontological and epistemological positions and in choosing appropriate research methods and methodologies. These paradigms include:
a). Positivism: Positivism asserts that knowledge is derived from observable phenomena and empirical evidence. It emphasizes objectivity, replicability, and the use of quantitative methods to test hypotheses.
b). Interpretivism: Interpretivism posits that knowledge is socially constructed through subjective experiences and interpretations. It focuses on understanding the meanings individuals attribute to their experiences, often using qualitative methods such as interviews, observations, and textual analysis.
c). Critical Realism: Critical realism seeks to bridge the gap between positivism and interpretivism by acknowledging the existence of an objective reality that is independent of human perception but also recognizing that our understanding of this reality is mediated through our perceptions and interpretations. It advocates for the exploration of underlying structures and mechanisms that generate observable phenomena while allowing for the influence of social contexts and human agency.
d). Constructivism: Constructivism proposes that knowledge is actively constructed by individuals based on their experiences and interactions with the world. It highlights the role of social and cultural contexts in shaping knowledge and emphasizes qualitative research methods that explore subjective meanings and interpretations.
e). Post-positivism: Post-positivism acknowledges the critiques of positivism while retaining its commitment to empirical observation and scientific vigor. It introduces concepts like theory-laden observation and the acknowledgment of researcher biases, aiming to refine positivist approaches to account for the complexities of social phenomena.
Navigating Different Philosophical Positions

Each philosophical position has implications for research design, methodology, data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Researchers must align their chosen paradigm with their research questions and objectives to ensure coherence and vigor in their studies. For instance:
1.Methodological Implications: Positivist research often employs quantitative methods to measure variables and test hypotheses, whereas interpretivist research favors qualitative methods to explore meanings and subjective experiences.
2. Ontological and Epistemological Assumptions: Understanding whether one believes in an objective reality (ontology) and how one believes knowledge is obtained and validated (epistemology) is crucial in selecting appropriate research methods and interpreting findings.
Advocating for Critical Realism
Critical realism emerges as a compelling philosophical stance that integrates insights from both positivism and interpretivism. It acknowledges the existence of an objective reality while recognizing that our understanding of this reality is mediated through social contexts, perceptions, and interpretations. Critical realism advocates for:
a) Causal Mechanisms: Exploring underlying structures and mechanisms that generate observable phenomena.
b) Contextual Understanding: Acknowledging the role of social contexts, historical conditions, and human agency in shaping phenomena.
c) Methodological Pluralism: Embracing a variety of research methods, both quantitative and qualitative, to capture different facets of complex social realities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating philosophical paradigms, ontology, and epistemology is essential for any researcher aiming to conduct rigorous and impactful research. By understanding these foundational concepts and choosing an appropriate philosophical stance such as critical realism, researchers can enhance the depth and validity of their studies. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of these concepts, empowering graduate students and researchers to articulate their research approaches confidently and contribute meaningfully to their fields of study.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
What is Anemia of Chronic Disease?

Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD), also known as anemia of inflammation or anemia of inflammation and chronic disease, is a prevalent condition often associated with chronic illnesses that last longer than three months and cause sustained inflammation. This form of anemia is particularly challenging because it not only stems from the chronic disease itself but also exacerbates the overall health burden on affected individuals.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of ACD is closely linked to the body’s inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation, which is a hallmark of many autoimmune diseases and long-term illnesses, significantly alters iron metabolism. Normally, iron is recycled from old red blood cells and used in the production of new ones. However, in ACD, inflammatory cytokines, particularly interleukin-6 (IL-6), stimulate the production of hepcidin, a hormone that regulates iron homeostasis. Hepcidin inhibits iron absorption in the gut and traps iron in macrophages, making it unavailable for red blood cell production, leading to a functional iron deficiency. Additionally, chronic inflammation can suppress erythropoiesis (the production of red blood cells) and reduce the lifespan of existing red blood cells, compounding the severity of anemia.
Epidemiology and Affected Populations
ACD is the second most common type of anemia after iron-deficiency anemia, particularly in populations over the age of 65. It is often seen in individuals with chronic conditions such as cancer, chronic kidney disease (CKD), heart failure, and a range of autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The prevalence of ACD in these populations highlights the importance of understanding and managing this condition effectively to improve overall patient outcomes.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical symptoms of ACD are often subtle and can overlap with those of the underlying chronic disease. Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pallor, shortness of breath, and dizziness. These symptoms may be exacerbated during physical activity. However, the mild nature of ACD symptoms means that the condition is often underdiagnosed or attributed solely to the chronic disease without recognizing the contribution of anemia.
Diagnosis and Laboratory Findings
Diagnosing ACD involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Blood tests are crucial for identifying the characteristic features of ACD, including low hemoglobin levels, normal or elevated serum ferritin (reflecting adequate iron stores), low serum iron, and low transferrin saturation. The reticulocyte count is typically low, indicating reduced erythropoiesis. In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be conducted to assess iron stores directly and rule out other causes of anemia.
Management and Treatment Strategies
The primary approach to managing ACD is to address the underlying chronic condition. Effective treatment of the chronic disease often leads to an improvement in anemia. However, in cases where the anemia is severe or the chronic disease is difficult to control, additional interventions may be necessary. These can include:
Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs): Synthetic forms of erythropoietin (EPO) can be administered to stimulate red blood cell production. This is particularly useful in patients with chronic kidney disease or cancer, where endogenous EPO production is impaired.
2 .Iron Therapy: Although oral iron supplementation is typically less effective in ACD due to hepcidin-induced iron sequestration, intravenous iron therapy may be beneficial, particularly when combined with ESAs.
3 .Blood Transfusions: In cases of severe anemia, blood transfusions may be required to rapidly increase hemoglobin levels. However, this is generally considered a short-term solution due to the potential risks of iron overload and transfusion-related complications.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While ACD itself may not be preventable due to its association with chronic diseases, patients can take steps to support overall health and potentially mitigate the severity of anemia. A balanced diet rich in iron (from sources such as lean meats and dark leafy greens), folate, vitamin B12, and vitamin C can support healthy red blood cell production. Regular monitoring of iron levels and timely medical intervention are essential in managing ACD effectively.
In conclusion, Anemia of Chronic Disease is a complex condition that requires a broad approach to diagnosis and management. Understanding the interplay between chronic inflammation and iron metabolism is key to effectively treating this form of anemia. Through careful management of the underlying disease and appropriate use of adjunct therapies, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of this condition.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
Management of Preeclampsia

Preeclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, emerging typically after the 20th week of gestation. It is distinguished by elevated blood pressure and potential multisystem involvement, most frequently affecting renal and hepatic functions. This condition presents significant risks for maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, necessitating keen monitoring, timely diagnosis, and appropriate management to ensure favorable outcomes for both mother and child.
Diagnostic Criteria and Processes
Clinical Criteria: The diagnosis of preeclampsia is confirmed when hypertension develops after 20 weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive woman, accompanied by one or more of the following indicators of organ dysfunction:
Proteinuria: Detection of protein in the urine, suggestive of renal impairment.
Renal Impairment: Other clinical indicators of compromised kidney function, such as increased serum creatinine.
Thrombocytopenia: A platelet count less than 100,000/microliter, indicative of platelet consumption or bone marrow suppression.
Hepatic Dysfunction: Elevated liver transaminases twice the normal concentration, reflecting hepatic injury.
Pulmonary Edema: Accumulation of fluid in the lungs, presenting as shortness of breath and hypoxemia.
Neurological Symptoms: New-onset, persistent headaches unresponsive to analgesics, or visual disturbances such as scotomata or blurred vision.
Blood Pressure Measurement: Blood pressure assessment in pregnancy involves measuring both systolic and diastolic pressures:
Systolic Pressure: A reading of 140 mm Hg or higher.
Diastolic Pressure: A reading of 90 mm Hg or higher.
For diagnostic confirmation, a second elevated reading taken at least four hours after the initial measurement is recommended.
Additional Diagnostic Tests: Upon suspicion of preeclampsia, a comprehensive evaluation is warranted, including:
Blood Tests: To assess liver enzymes, kidney function, and platelet count.
Urine Analysis: Either a 24-hour urine collection or a spot urine protein-to-creatinine ratio to evaluate protein excretion and renal function.
Fetal Ultrasound: Regular monitoring of fetal growth and amniotic fluid volume to assess intrauterine conditions.
Nonstress Test and Biophysical Profile: To evaluate fetal well-being through heart rate monitoring and ultrasound assessment of fetal movements, muscle tone, breathing, and amniotic fluid volume.
Management Strategies
Primary Management: The primary goal in managing preeclampsia is to balance prolonging the pregnancy to allow for fetal maturation with the risks posed to maternal and fetal health. This often involves a combination of close monitoring and medical interventions to control blood pressure and prevent complications.
Management of Mild Preeclampsia:
Outpatient Monitoring: Regular prenatal visits to monitor blood pressure, symptoms, and fetal health.
Home Monitoring: Daily self-monitoring of blood pressure and symptom tracking to detect any signs of disease progression.
Management of Severe Preeclampsia:
Hospitalization: For intensive monitoring of maternal and fetal well-being. This includes frequent blood pressure checks, laboratory tests, and fetal monitoring.
Pharmacotherapy:
Antihypertensive Medications: Such as labetalol, nifedipine, or methyldopa to control blood pressure.
Anticonvulsants: Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice to prevent eclamptic seizures.
Corticosteroids: Administered to enhance fetal lung maturity if preterm delivery is anticipated.
Timing and Method of Delivery:
Delivery Timing: The timing of delivery is critical and depends on the severity of the condition, gestational age, and the health of both mother and fetus.
Mild Preeclampsia: Delivery is generally recommended after 37 weeks of gestation.
Severe Preeclampsia: May necessitate delivery before 37 weeks to prevent serious maternal and fetal complications.
2. Method of Delivery: Decided based on clinical factors, with vaginal delivery preferred if conditions allow. However, a cesarean section may be necessary for severe cases or if labor induction fails.
Postpartum Care
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Postpartum monitoring is crucial as preeclampsia can persist or even develop after delivery, known as postpartum preeclampsia. This involves:
Close Monitoring: Regular assessment of blood pressure and symptoms in the immediate postpartum period.
Patient Education: Informing patients about the signs and symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia, such as severe headaches, visual changes, epigastric pain, and nausea or vomiting, and advising them on when to seek urgent medical care.
Long-Term Follow-Up: Regular follow-up visits to monitor blood pressure and assess for potential long-term cardiovascular and renal implications of preeclampsia.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
How to Write a Case Study

The case study indulges into the ideal process of rehabilitating a semi-professional cyclist who underwent a traumatic transfemoral amputation due to a road traffic accident. This comprehensive analysis aims to shed light on the complexities of limb loss rehabilitation, emphasizing the importance of tailored interventions and evidence-based practice in optimizing outcomes for individuals facing similar challenges.
Client Characteristics

In this section, a detailed exploration of the patient’s background, lifestyle, and medical history provides crucial insights into his unique rehabilitation needs. Emphasis is placed on the impact of the accident on the patient’s physical and psychological well-being, as well as his aspirations for returning to an active lifestyle post-amputation.
The patient, a previously healthy 24-year-old male, was actively engaged in semi-professional cycling and held a physically demanding job at a bicycle shop. The road traffic accident resulted in a traumatic transfemoral amputation, significantly altering his physical capabilities and emotional state. His aspirations to return to his previous level of physical activity underscore the importance of addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of his rehabilitation journey.
Examination Findings
A thorough examination is conducted to assess the patient’s physical condition and identify areas of impairment resulting from the amputation. Objective measurements, including strength assessments and gait analysis, complement subjective reports of phantom limb pain and functional limitations, forming the basis for the subsequent formulation of a clinical hypothesis.
The examination reveals significant impairments in strength and mobility, as well as the presence of phantom limb pain, which negatively impacts the patient’s daily life and rehabilitation progress. These findings highlight the need for a comprehensive treatment approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the patient’s condition.
Clinical Hypothesis/Impression

Drawing on current research and clinical expertise, the clinical hypothesis focuses on addressing the patient’s complex pain experience and psychological distress following the amputation. The identification of neuropathic pain mechanisms and the potential efficacy of interventions such as mirror therapy and mental imagery inform the development of a tailored treatment plan aimed at promoting pain relief and enhancing functional recovery.
The clinical hypothesis highlights the importance of addressing the underlying causes of the patient’s pain and implementing evidence-based interventions to optimize his rehabilitation outcomes. By targeting both the physical and psychological aspects of his condition, the treatment plan aims to improve the patient’s overall quality of life and facilitate his successful return to daily activities.
Intervention
The intervention plan is majorly crafted to address the patient’s unique rehabilitation goals and challenges. A multi-disciplinary approach, incorporating pharmacological interventions, prosthetic care, and psychological support, is implemented to optimize outcomes and empower the patient in his journey towards recovery. Detailed descriptions of specific treatment modalities and their rationale are provided, highlighting the importance of individualized care and ongoing monitoring throughout the rehabilitation process.
The intervention plan includes a combination of pharmacological management, prosthetic fitting and training, and psychological support to address the patient’s physical and psychological needs. Each component of the plan is tailored to the patient’s specific goals and challenges, with regular monitoring and adjustments made to ensure optimal outcomes.
Outcome
Objective measures are used to track the patient’s progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the intervention plan. Significant improvements in pain management, functional mobility, and quality of life are observed over the course of treatment, with particular emphasis on the transformative impact of mirror therapy on the patient’s pain experience and overall well-being. The importance of ongoing follow-up and support is emphasized as integral to maintaining long-term gains and facilitating the patient’s successful reintegration into daily activities.
The patient demonstrates significant improvements in pain management, functional mobility, and overall quality of life following the implementation of the intervention plan. Objective measures, including pain intensity ratings and functional assessments, demonstrate tangible improvements in the patient’s physical and psychological well-being, highlighting the effectiveness of the multi-disciplinary approach employed in his rehabilitation.
Discussion
A comprehensive discussion examines the broader implications of the case study for physiotherapy practice, highlighting the importance of holistic rehabilitation approaches that address the complex interplay of physical, psychological, and social factors in individuals with limb loss. Key lessons learned from the case study, including the value of evidence-based practice and the need for ongoing collaboration between healthcare professionals, are discussed in relation to optimizing outcomes and promoting patient-centered care.
The discussion explores the broader implications of the case study for physiotherapy practice, emphasizing the importance of adopting a holistic approach to rehabilitation that addresses the complex needs of individuals with limb loss. By integrating evidence-based interventions and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare professionals can enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation interventions and improve outcomes for patients with limb loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the extended case study provides a detailed exploration of the rehabilitation journey of a semi-professional cyclist following a traumatic limb amputation. Through a comprehensive analysis of client characteristics, examination findings, intervention strategies, and outcomes, valuable insights are gained into the complexities of limb loss rehabilitation and the importance of personalized, evidence-based care in achieving optimal outcomes for individuals facing similar challenges.
The case study underscores the importance of adopting a holistic approach to rehabilitation that addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of limb loss by focusing on interventions to the unique needs of each patient and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare professionals can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals with limb loss.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
Leukemia in Children

Introduction
Leukemia in children presents a formidable challenge, demanding meticulous management and treatment. This detailed discussion aims to devolve into various facets of childhood leukemia, encompassing its definition, types, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment modalities, potential complications, preventive measures, and strategies for supporting a child living with leukemia.
Understanding Leukemia in Children

1. Definition
Leukemia is a hematological malignancy affecting the blood and bone marrow. Its prominence in childhood stems from the rapid proliferation of abnormal blood cells, disrupting the delicate balance within the body.
2. Types of Blood Cells
Understanding the roles of
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.platelets (thrombocytes), and
3.white blood cells (leukocytes)
Is fundamental. An imbalance in these cells results in a spectrum of symptoms, from anemia to increased infection susceptibility.
3. Types of Leukemia

. Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): Predominant in children.
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML): The second most common type.
Hybrid or Mixed Lineage Leukemia: A rare amalgamation of ALL and AML.
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML): Uncommon in children.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Extremely rare in pediatric cases.
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML): A rare type with unique growth characteristics.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Causes
The exact etiology of childhood leukemia remains elusive. Genetic mutations in bone marrow cell genes may occur sporadically or, in some instances, be inherited.
2. Risk Factors
Exposure to Radiation.
Particularly high levels.
Inherited Syndromes.
Down syndrome.
Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Immune System Conditions.
Inherited disorders affecting immune function.
Family History.
Having a sibling with leukemia elevates the risk.
Symptoms of Leukemia in Children
A diverse array of symptoms underscores leukemia’s impact on children, including;
.Pale skin
. Fatigue
.Dizziness
.Headaches
.Shortness of breath
.Frequent infections
.Fever
. Easy bruising
.Bleeding
.Bone or Joint pain, and
.Abdominal swelling.
Diagnosis:
1. Procedures:
.Blood Tests (Complete Blood Count — CBC): Essential for initial assessment.
Bone Marrow Aspiration or Biopsy: Crucial in detecting leukemia cells.
Lab Tests: Precisely determine leukemia type.
Diagnostic Imaging: X-rays, ultrasound,
lymph node biopsy, and
Lumbar puncture offer a comprehensive diagnostic perspective.
2. Classification
Unlike other cancers, leukemia is not staged but rather classified into groups, subtypes, or both based on type and specific characteristics, aiding in targeted treatment approaches.
Treatment Options:
1. Primary Treatments:
Blood Transfusions: Address low blood counts, bleeding, or infections.
Chemotherapy: The mainstay, killing or inhibiting cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays to target and eradicate cancer cells.
Stem Cell Transplant: Involves high-dose chemotherapy followed by stem cell replacement.
Targeted Therapy: Specific medications tailored to combat certain types of leukemia.
Immunotherapy: Enhances the body’s immune system to combat cancer cells.
Complications:
1. Short-term:
Serious Infections: Resulting from compromised immune function.
Severe Bleeding: A consequence of low platelet levels.
Thickened Blood: Accumulation of leukemia cells in the bloodstream.
2. Long-term:
Leukemia Recurrence: A persistent concern.
Development of Other Cancers: A potential consequence of treatment.
Heart and Lung Problems: Arising from the impact of leukemia or its treatment.
Learning Issues and Growth Delays: Impacts on cognitive development and physical growth.
Fertility Problems and Bone Issues: Osteoporosis as a potential long-term complication.
Prevention:
Preventing childhood leukemia remains challenging, with a focus on caution regarding unnecessary exposure to radiation, especially in diagnostic procedures involving pregnant women and children.
Supporting a Child with Leukemia:
1. Ongoing Care:
Regular visits to oncologists and healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring and addressing emerging issues.
2. Balanced Lifestyle:
Managing eating difficulties and encouraging appropriate exercise play a vital role in supporting overall health.
3. Emotional Support:
Seeking counseling or participating in support groups helps both the child and their family navigate the emotional challenges associated with leukemia.
4. Follow-up Appointments:
Attending all scheduled appointments ensures continuous monitoring and timely intervention if complications arise.
When to Contact Healthcare Provider:
Prompt communication with healthcare providers is essential if the child experiences fever, worsening symptoms, new symptoms, or side effects from treatment.
Key Points Summary:
Leukemia necessitates a comprehensive approach, involving diagnosis, tailored treatment, and ongoing monitoring.
Varied symptoms demand timely medical attention for an optimal prognosis.
Treatment modalities, including chemotherapy and stem cell transplant, are tailored to the specific leukemia type.
Complications, both short-term and long-term, underscore the importance of ongoing follow-up care.
Prevention is limited, with a focus on minimizing unnecessary radiation exposure.
Comprehensive support, encompassing medical, emotional, and lifestyle aspects, is essential for the child’s well-being.
Next Steps:
1. Follow-up Care:
Continued regular check-ups and imaging tests remain integral to post-treatment monitoring.
2. Communication:
Maintaining open and transparent communication with healthcare providers ensures timely intervention if issues arise.
3. Research:
Inquiring about ongoing clinical trials or new treatments enables families to stay informed about emerging possibilities.
Conclusion:
Childhood leukemia mandates a collaborative effort from medical professionals, caregivers, and support networks to optimize outcomes and enhance the quality of life for affected children. As the landscape of pediatric oncology evolves, the commitment to advancing treatment options and minimizing the impact of complications remains paramount, offering hope for a brighter future for children navigating the complexities of leukemia.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance
Blood cell

The blood cells serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of hematopoiesis, the process through which various blood cell types are formed and function in the human body. This detailed discussion aims to unravel the key aspects presented in the article, delving into the structure, functions, and disorders associated with;
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.White blood cells (leukocytes), and
platelets (thrombocytes).
Blood Cell Types and Composition
At the core of the circulatory system lie three major types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cellular components collectively contribute to 45% of blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% being plasma. This delicate balance underscores the dynamic nature of blood, serving as a conduit for various vital functions within the body.
1.Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
The discussion commences with a focus on red blood cells, the primary carriers of oxygen in the bloodstream. Erythrocytes, characterized by their unique biconcave shape and lack of a nucleus, play a crucial role in gas exchange facilitated by the iron-containing protein hemoglobin. The intricate details of erythropoiesis, the process of RBC formation in the red bone marrow, offer a glimpse into the remarkable physiological mechanisms that ensure a constant supply of oxygen carriers. The staggering production rate of 2.4 million RBCs per second in adults highlights the body’s continuous demand for these essential cells. The information regarding the lifespan of RBCs (100–120 days) and their subsequent removal by the spleen adds another layer to our understanding of the life cycle of these vital cells. The absence of a nucleus in mature red blood cells, a unique characteristic among human cells, is highlighted. The pathological conditions of anemia and polycythemia are thoroughly explored, shedding light on the consequences of an imbalance in red blood cell count. Additionally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) provides valuable insights into the diagnostic tools used in assessing the health of red blood cells.
2.White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
The immune system, our body’s defense mechanism, relies on white blood cells to combat infectious diseases and foreign materials. These leukocytes, originating from multipotent cells in the bone marrow, are categorized into granulocytes (basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). The discussion delves into the roles these distinct white blood cell types play in the human immune system, offering a nuanced understanding of their functions. The conditions of leukopenia and leukocytosis, indicating low and high white blood cell counts, respectively, are explored, emphasizing the diagnostic significance of monitoring these counts. The increased white blood cell count during infections and its association with hematological cancers underscore the pivotal role leukocytes play in our overall health.
3.Platelets (Thrombocytes)
The section on platelets elucidates their role in hemostasis, the process of preventing and stopping bleeding. These small, irregularly shaped cell fragments, derived from megakaryocytes, circulate in the blood and are essential for the formation of blood clots. The average lifespan of platelets, a mere 5 to 9 days, emphasizes the continuous production required for maintaining hemostatic balance. The normal range of platelet counts and the potential consequences of low or high platelet numbers provide valuable insights into the delicate equilibrium necessary for preventing excessive bleeding or the formation of thrombosis. Thrombocytopathy, a broad term encompassing disorders related to platelets, is discussed, including thrombocytopenia, thrombasthenia, and thrombocytosis. The intricate relationship between platelets and growth factors, as well as their role in wound healing, showcases the multifaceted contributions of these small but crucial cellular fragments.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): The article introduces the Complete Blood Count (CBC) as a vital diagnostic tool providing a comprehensive analysis of blood cell composition. The historical transition from manual counting to automated analyzers reflects the evolving landscape of medical technology, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of blood cell analysis. The significance of CBC in offering an overview of a patient’s general health status is underscored, emphasizing its widespread use in medical diagnostics.
Historical Discoveries.
The historical perspective woven into the article traces the evolution of our understanding of blood cells. From Jan Swammerdam’s pioneering observation of red blood cells in 1658 to Paul Ehrlich’s techniques in staining blood films and differential blood cell counting in 1879, the narrative highlights key milestones in the establishment of hematology as a distinct field of medicine. The contributions of various scientists, including Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Alfred Donne, and Gabriel Andal, collectively shaped our current knowledge of blood cells.
Conclusion
The blood cells provides a rich tapestry of information encompassing their structure, functions, and associated disorders. It serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the dynamic nature of blood and the pivotal roles played by red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in maintaining homeostasis within the human body. The integration of historical discoveries adds depth to the narrative, highlighting the continuous quest for knowledge that has defined the field of hematology. This article not only serves as an educational tool but also showcases the remarkable advancements in medical science and technology that have propelled our understanding of blood cells to new heights. As we unravel the mysteries of hematopoiesis, we gain valuable insights into the machinery that sustains life within our veins.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
10 Simple Tips for Caring for Your Heart.

The heart, a tireless worker at the core of our well-being, demands our attention and care. As we navigate through Heart Health Month this February, let’s explore ten simple yet impactful tips to ensure our hearts thrive. These practices, ranging from physical activity to laughter and dental hygiene, collectively contribute to a holistic approach to cardiovascular wellness.
1.Cardiovascular Exercise: A Heart’s Best Friend
Engaging in regular cardiovascular or aerobic activities is fundamental for heart health. Following the American Heart Association’s recommendations of 75 minutes of vigorous exercise or 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly can significantly boost cardiorespiratory fitness. Activities such as running, cycling, or brisk walking not only elevate heart rate but also enhance overall cardiovascular function. The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles during exercise contribute to improved blood flow and reduced strain on the heart.
2.Embrace a Smoke-Free Lifestyle
Quitting smoking is a paramount step in safeguarding your heart. Smoking damages both the heart and blood vessels, escalating the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, avoiding second-hand smoke is crucial, as it has been linked to heart attacks and strokes. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke lead to the narrowing of blood vessels, increasing the workload on the heart and elevating the risk of high blood pressure.
3.Prioritize Quality Sleep
Adequate sleep, often underestimated, plays a pivotal role in heart health. With at least seven hours of nightly rest, blood pressure lowers, and the body undergoes essential repair processes. Research underscores the correlation between poor sleep and heightened risks of high blood pressure, subsequently increasing the likelihood of heart diseases. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a conducive sleep environment are crucial steps in promoting optimal cardiovascular health.
4.Regular Checkups: A Heart-Healthy Habit
Consistent visits to the doctor for heart health checkups are essential. Assessing risk factors such as diet, blood pressure, cholesterol, and family history enables early detection and management of potential issues. A proactive approach to heart health empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices. Regular checkups also provide an opportunity for healthcare professionals to offer personalized guidance on maintaining heart health through tailored interventions.
5.Laughter: The Heart’s Natural Tonic
Laughing, whether through entertainment or social interactions, yields surprising benefits for the heart. The act of laughter reduces artery inflammation, lowers stress hormones, and increases levels of good cholesterol. Integrating humor into daily life becomes a delightful prescription for heart health. Laughter promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good chemicals, which contribute to overall well-being and stress reduction.
6.Dental Hygiene and Heart Connection
Surprising as it may seem, maintaining good dental hygiene contributes to heart health. Studies reveal a link between poor dental health and the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream, impacting heart valves. Simple practices such as regular brushing can significantly decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, regular dental checkups not only preserve oral health but also serve as a preventive measure against potential cardiovascular complications.
7.Fuel Your Heart with a Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, whole grains, vegetables, and legumes significantly improves blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Steering clear of salty foods and saturated fats is crucial, as they contribute to elevated blood pressure and increased bad cholesterol. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, further supports heart health by reducing inflammation and promoting optimal functioning of blood vessels.
8.Maintaining a Healthy Weight: A Heart’s Delight
Striving for and maintaining a healthy weight is a powerful defense against heart disease and high blood pressure. A combination of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and mindful calorie intake promotes overall well-being and cardiovascular health. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, leading to conditions such as hypertension and diabetes. Adopting sustainable lifestyle changes, including portion control and regular physical activity, contributes to achieving and sustaining a healthy weight.
9.Hydration: The Heart’s Elixir
Staying adequately hydrated is a simple yet often overlooked aspect of heart care. Considering the heart’s continuous effort in pumping around 2,000 gallons of blood daily, increased water intake supports its optimal functioning. Dehydration can lead to thicker blood, making the heart work harder to pump blood through the vessels. Maintaining proper hydration levels ensures the efficient transport of nutrients and oxygen to cells, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
10.Stay Active, Break Inactivity
Combatting sedentary lifestyles is crucial in preserving heart health. Incorporating simple changes like taking the stairs, walking, playing with pets, or engaging in household chores helps keep the heart active, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Prolonged sitting has been associated with various health risks, including obesity and heart disease. Regular physical activity not only supports cardiovascular health but also contributes to weight management and overall well-being.
In conclusion, adopting these ten heart-healthy habits provides a comprehensive approach to cardiovascular wellness. Whether it’s the joyous act of laughter, the discipline of regular exercise, or the mindfulness of a balanced diet, each step contributes to the harmonious symphony of a healthy heart. As we celebrate Heart Health Month, let’s embrace these practices and gift our hearts the care they deserve. Through consistent efforts and lifestyle modifications, we can ensure that our hearts continue to beat with vitality and resilience.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
The pathophysiology of hypertension

Introduction
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a complex medical condition affecting a significant proportion of the global population. Despite its prevalence, there remains uncertainty regarding its pathophysiology, with essential hypertension constituting a substantial portion where no single identifiable cause is found. This comprehensive discussion aims to delve into the physiological mechanisms involved in the development of hypertension, exploring factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic factors, and intrauterine influences.
Cardiac Output and Peripheral Resistance

Maintaining normal blood pressure relies on the delicate balance between cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance. Essential hypertension often involves a normal cardiac output but elevated peripheral resistance, primarily determined by small arterioles. The role of smooth muscle cells, calcium concentration, and structural changes in arteriolar vessel walls contribute to the irreversible rise in peripheral resistance.
Renin-Angiotensin System

The renin-angiotensin system plays a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. Renin, released in response to various stimuli, initiates the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. This system also stimulates aldosterone release, promoting sodium and water retention. While the circulating system may not be directly responsible for essential hypertension, local renin-angiotensin systems in organs like the kidney, heart, and arterial tree gain significance in regulating regional blood flow.
Autonomic Nervous System

Sympathetic nervous system stimulation affects arteriolar constriction and dilation, playing a pivotal role in maintaining normal blood pressure. Although the exact role of epinephrine and norepinephrine in hypertension etiology remains unclear, drugs blocking the sympathetic nervous system demonstrate therapeutic efficacy.
Endothelial Dysfunction

Vascular endothelial cells, producing vasoactive agents like nitric oxide and endothelin, play a key role in cardiovascular regulation. Endothelial dysfunction, implicated in essential hypertension, involves impaired production of nitric oxide. This dysfunction, once established, becomes irreversible, highlighting its primary nature in hypertension.
Vasoactive Substances

Various vasoactive substances, such as bradykinin, endothelin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and ouabain, influence sodium transport and vascular tone. These substances contribute to the delicate balance in maintaining normal blood pressure.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition significantly contributes to hypertension, with specific mutations linked to disorders like Liddle’s syndrome, glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism, and others. The intricate interplay of multiple genes makes it challenging to pinpoint individual contributions.
Intrauterine Influences
Fetal influences, particularly birth weight, emerge as determinants of adult blood pressure. The Barker hypothesis suggests a link between low birth weight, metabolic abnormalities, and hypertension in later life. However, the role of genetic factors in this relationship requires further exploration.
Diastolic Dysfunction

Hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy leads to impaired diastolic relaxation, affecting ventricular input during exercise. This dysfunction contributes to increased atrial pressure, pulmonary congestion, atrial fibrillation, and potential complications like pulmonary edema.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the pathophysiology of hypertension involves exploration of various physiological mechanisms. While essential hypertension remains a complex and often multifactorial condition, advancements in research shed light on factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic influences, and intrauterine factors. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and preventive measures against the global burden of hypertension.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
Cervical Cancer

Introduction
Cervical cancer is a significant health concern affecting women worldwide. It arises from abnormal cell growth in the cervix, often linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Despite advancements in prevention and treatment, cervical cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women. Understanding its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial for early detection and effective management.
1. Understanding Cervical Cancer

Cervical cancer originates in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina.
HPV, a common sexually transmitted infection, is a primary cause of cervical cancer, with certain strains posing higher risks.
The body’s immune response typically clears HPV infections, but persistent infections can lead to cervical cell abnormalities and eventually cancer.
2. Symptoms and Diagnosis

Cervical cancer may not present noticeable symptoms initially, making regular screenings essential for early detection.
Symptoms can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and unusual discharge.
Diagnostic methods include Pap tests, HPV DNA testing, colposcopy, and biopsy to confirm cervical cancer and determine its stage.
3. Treatment Options

Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, size, and type, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
Surgical interventions, such as hysterectomy or removal of cancerous tissue, are common for early-stage cervical cancer.
Advanced stages may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy to eliminate cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
4. Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors increase the risk of developing cervical cancer, including HPV infection, smoking, early sexual activity, and weakened immune system.
Prevention strategies include HPV vaccination, routine Pap tests for early detection of precancerous lesions, practicing safe sex, and smoking cessation.
5. Impact on Women’s Health

Cervical cancer not only affects physical health but also has emotional, social, and financial repercussions on women and their families.
Access to screening, vaccination, and treatment services significantly impacts the prognosis and survival rates of women diagnosed with cervical cancer.
Addressing disparities in healthcare access and promoting awareness about cervical cancer prevention are crucial for improving women’s health outcomes globally.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer remains a significant public health challenge despite advancements in prevention and treatment. Early detection through regular screenings and vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the burden of this disease. Moreover, addressing risk factors such as smoking and promoting safe sexual practices are vital for cervical cancer prevention. By raising awareness, improving access to healthcare services, and advocating for comprehensive cervical cancer prevention programs, we can strive towards reducing the incidence and mortality associated with this preventable disease, ultimately enhancing women’s health and well-being worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
First Aid Instructions for 10 Medical Emergencies

Introduction
First aid is the immediate care provided to a sick or injured person, often serving as a crucial bridge until professional medical help arrives. While formal first aid training is ideal, there are basic life-saving steps that everyone should be aware of. This article outlines first aid instructions for 10 common medical emergencies, along with practical tips and a comprehensive first aid kit list.
1.Stopped Heart (Cardiac Arrest)

In the event of a stopped heart, immediate action is crucial:
Initiate CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) to maintain blood circulation.
Use an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available to shock the heart.
Call 911 and continue care until professional help arrives.
2. Bleeding

Effective bleeding control is essential
Apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to control bleeding.
Elevate the bleeding body part if possible to reduce blood flow.
Seek immediate medical help for severe bleeding.
3. Choking
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*acrWmV_gxPmZh9JX
Swift response is vital when someone is choking:
Perform the Heimlich maneuver for a conscious choking victim.
If unconscious, initiate CPR and call for help.
Monitor airway and breathing.
4. Burns
Proper handling of burns is crucial for minimizing damage:
Stop the burning process by cooling the burn with running water.
For minor burns, use a light gauze bandage and avoid breaking blisters.
Seek medical attention for severe burns.
5. Blisters
Appropriate care can aid in the healing of blisters:
Leave small, unopened blisters alone to promote healing.
For larger, painful blisters, clean, drain, and apply antibiotic ointment.
Monitor for signs of infection.
6. Broken Bone/Fracturey
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*4NouIgQSR_QHj-t6.jpeg
Careful management of fractures is essential:
Call 911 for severe fractures and avoid moving the person if a spinal injury is suspected.
Immobilize the injured area with a splint, elevate, and apply a cold pack for pain.
Seek prompt medical attention.
7. Sprains
Proper first aid can alleviate symptoms of sprains:
Rest the injured limb, apply a cold pack, and elevate if possible.
Seek medical attention for severe pain, inability to bear weight, or signs of infection.
Follow R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) principles.
8. Nosebleeds
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*jJd3qZg5Q8xI_IHf
Effective nosebleed management is essential:
Lean forward and pinch the nose just below the bridge to control bleeding.
Apply a cold pack and seek medical attention for persistent or frequent nosebleeds.
Address underlying causes such as dry air or trauma.
9. Frostbite
Timely response is critical to treating frostbite:
Get out of the cold and gradually warm the affected area with warm water.
Avoid rubbing the affected area, and do not use dry heat sources.
Seek medical attention for severe cases.
10. Bee Sting
Proper care for bee stings is vital, especially for allergic reactions:
Remove the stinger immediately using a straight-edged object.
Monitor for signs of an allergic reaction and call 911 if necessary.
Clean the area, apply a cold pack, and use antihistamines for swelling.
First Aid Kit List
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*WM_HfAvd_-O5fZMC
A well-prepared first aid kit is an essential tool for handling emergencies. The kit should include:
Adhesive bandages in various sizes and shapes
Gauze pads and compress dressings
Adhesive cloth tape, latex gloves, and antiseptic wipes
Antibiotic ointment and hydrocortisone ointment
A breathing barrier for performing CPR
Instant cold compress, tweezers, and an oral thermometer
Emergency blanket for warmth and comfort
Conclusion
While formal first aid training is highly recommended, understanding the basics of immediate care can make a significant difference in emergencies. The outlined first aid instructions cover a range of medical situations, and having a well-stocked first aid kit further enhances preparedness. Quick and appropriate action can be a crucial factor in saving lives during medical emergencies. Remember, being informed and ready can make you a valuable first responder in times of need.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance and guidance
14 Reasons to become a Doctor

Introduction
Embarking on a career as a doctor is a monumental commitment, requiring an extensive education, unwavering dedication, and resilience. This detailed exploration aims to involve deep into the 14 compelling reasons to choose the noble profession of a medical doctor. Each reason represents a reality of the face and nature of the medical field, elucidating the diverse experiences, responsibilities, and its rewards associated with this esteemed profession.
1.To Help Others
At the core of a doctor’s vocation lies the fundamental responsibility to save lives and enhance the health of their patients. Exploring through challenging moments in patients’ lives, doctors have a unique opportunity to contribute significantly to their recovery and overall well-being. This shown aspect forms the very heart of the medical profession, acting as a profound motivator for those who choose this career path
2. To Explore Science

The steps involving to become a doctor unfolds as a rigorous educational stages across various scientific disciplines. From foundational studies in physics, chemistry, and biology during undergraduate education to the exploration of specialized subjects like pharmacology, anatomy, pathology, and neurology in medical school, doctors engage with an expansive array of scientific knowledge. This profession not only broadens their understanding but also empowers them to apply scientific principles practically in the life of patient care.
3 .To Have Variety in Your Work
A career in medicine is anonymously dynamic, promising a different experience each day. Doctors find themselves at the forefront of a diverse condition of illnesses and injuries, prompting the utilization of various skills and treatments. This extends beyond the medical cases to include interactions with a wide group of people, including patients, families, and colleagues, making the profession continuously admiring and intellectually engaging.
4. To Collaborate
The medical profession thrives on a team-oriented environment, fostering collaboration with nurses, orderlies, administrators, specialists, and pharmacists. This collaborative ethos not only promotes continuous learning as doctors share insights but also serves as a critical for finding collective solutions to complex medical conditions. Effective teamwork emerges as a cornerstone for successful patient care.
5.To Have Purpose in Your Work

Doctors occupy a crucial role in society, profoundly impacting the lives of individuals and their families. By promoting healthier lifestyles and improving patient health, doctors become stewards in contributing to the well-being of their communities. This sense of purpose adds a profound dimension to the daily work of a doctor.
6. To Educate
With their detailed study, doctors become experts of knowledge, which they can share with patients and colleagues as well. Patient education on health management and lifestyle improvements becomes a crucial aspect of a doctor’s responsibilities. Additionally, some doctors have the unique opportunity to contribute to medical education by mentoring and teaching medical students in teaching hospitals to get the best knowledge.
7. To Have Job Security
The universal demand for medical expertise provides doctors with a reassuring sense of job security. Unlike some professions, doctors rarely face concerns about a lack of competition for their skills. This extensive demand allows for greater flexibility when choosing a work location, catering to a broader spectrum of professional opportunities.
8. To Earn a Good Salary
While salaries in the medical field may vary based on factors such as location, experience, and specialization, doctors generally enjoy competitive remuneration coupled with excellent benefits. Specialized fields, particularly surgery, can qualify for even higher incomes. The financial rewards reflect the substantial investment of time and dedication required in pursuing of a medical career.
9. To Be a Leader

A medical career aligns seamlessly with the aspirations of individuals attached towards leadership roles. Physicians and surgeons often find themselves leading large teams of medical personnel, providing vital and main guidance while taking responsibility for patient outcomes. Exceptional leadership skills may present opportunities for doctors to pursue supervisory roles, further enriching their professional journey.
10. To Learn
Medical professionals encounter many challenges facing new medical conditions and dangers regularly. Liaising with experienced physicians and exposure to diverse cases contribute to a continuous learning environment. This commitment to lifelong learning renders a medical career particularly appealing to those with an insatiable passion for acquiring knowledge.
11. To Test Yourself
The study towards being a doctor is worth undertaking, marked by numerous challenges. Overcoming these challenges becomes a crucial for personal and professional growth. Adapting and continuous self-improvement emerge as integrated face of a physician’s journey, contributing to the development of resilient and resourceful medical professionals.
12. To Solve Problems
Critical thinking stands as a cornerstone of medical practice. Physicians accurately analyze symptoms, review patient conditions, and develop precise diagnosis, considering individual’s symptoms and clinical presentation of a disease condition. The expertise skills required in medicine demand cautiousness , structured thinking, and a balanced approach to well being , proofing the analytical competency of doctors.
13. To Contribute to Breakthroughs
Medicine, like many other scientific fields, is in a delicate state of expanding aided by technological advancements. Staying ahead of recent developments is not just a professional necessity but also an opportunity for doctors to contribute actively to breakthroughs in medical science. Those with an admiration towards medical innovation can explore positions in research hospitals, where their contributions may shape the future of healthcare.
14. To Find New Opportunities
Upon completing the rigorous phases of medical school and residency, doctors find themselves at a point of diverse opportunities. The array of choices includes pursuing specialization in a preferred field, opening a private practice, engaging in community work overseas, majoring into scientific research, contributing to public health initiatives, or transitioning into teaching positions, exploiting the versatility of a medical career.
Conclusion:
A career as a doctor is a field attached with diverse experiences, responsibilities, and opportunities. The 14 reasons explored in this discussion shed light on the main rewards and challenges that accompany the study of a medical profession. From the known satisfaction derived from helping others to the demand for knowledge and the potential to actively contribute to important developments, a medical career beckons those with indriven passion, full dedication, and a commitment to the continuous evolution of their professional journey. The resilience, adaptability, and sense of purpose implanted in the medical profession form the foundation of a vocation that extends far beyond the sense of a mere job, defining a passion that motivates those who aspire to make a meaningful impact on the lives of others through the practice of medicine.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for assistance guidance.
Digestive System

The digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrating the journey of food through the body, from the moment it enters the mouth to its exit through the anus. This complex process involves a network of organs, each playing a crucial role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the anatomy, functions, common conditions, care practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention for digestive system issues.
Anatomy of the Digestive System

Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract:
1.Mouth:
Initiating Digestion: Salivary glands activate as the sight and scent of food trigger the digestive process.
Chewing and Mixing: Food is chewed into digestible pieces, mixed with saliva to facilitate breakdown.
Swallowing: The tongue propels the food into the throat and esophagus.
2. Esophagus:
Transportation: A muscular tube conducting food to the stomach through peristalsis.
Sphincter Function: The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow food entry and contracts to prevent stomach content reflux.
3.Stomach:
Container and Mixer: A hollow organ holding and mixing food with stomach enzymes for further breakdown.
Acid Secretion: Cells in the stomach lining secrete powerful acids and enzymes crucial for digestion.
Release to Small Intestine: Processed stomach contents move to the small intestine for further digestion.
4.Small Intestine:
Segments and Functions: Comprising the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each segment has distinct roles in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Enzymatic Breakdown: Pancreatic enzymes and bile from the liver aid in breaking down food.
Nutrient Absorption: The jejunum and ileum absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
Consistency Changes: Contents transition from semi-solid to liquid as water, bile, enzymes, and mucus contribute to the process.
Biliary System

a. pancreas:
Enzyme Secretion: Releases digestive enzymes into the duodenum to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Insulin Production: The pancreas produces insulin, a key hormone for sugar metabolism.
b. Liver:
Nutrient Processing: Processes nutrients absorbed by the small intestine.
Bile Production: Secretes bile into the small intestine, aiding in fat digestion and vitamin absorption.
Detoxification: Acts as the body’s chemical “factory,” detoxifying harmful substances.
c. Gallbladder:
Bile Storage: Stores and concentrates bile from the liver.
Release into Duodenum: Releases bile into the duodenum to assist in fat absorption.
Large Intestine (Colon):
Colon:
Waste Processing: Responsible for transforming waste into a convenient form for bowel movements.
Peristalsis: Propels stool through the colon, removing water and transitioning it from a liquid to a solid state.
Storage and Elimination: Stool is stored in the sigmoid colon until mass movements propel it into the rectum for elimination.
Rectum:
Chamber Function: A straight chamber connecting the colon to the anus.
Signaling and Holding: Signals the brain about stool presence and holds stool until evacuation.
Anus:
Final Elimination: The last part of the digestive tract, consisting of pelvic floor muscles and sphincters.
Sphincter Control: Surrounding sphincter muscles control stool release, preventing involuntary bowel movements.
Conditions and Disorders
Digestive system health can be affected by a spectrum of conditions, ranging from temporary issues to chronic diseases:
Temporary Conditions:
Constipation:
Frequency and Characteristics: Reduced bowel movements with dry and hard stool.
Difficulty and Pain: Straining during bowel movements, leading to discomfort.
2.Diarrhea:
Loose and Watery Stool: Abnormal stool consistency often caused by various factors.
Potential Causes: Bacterial infections, dietary issues, or unknown triggers.
3.Heartburn:
Misleading Name: Despite the name, heartburn is a digestive issue.
Acidic Backflow: Occurs when stomach acids move up the esophagus, causing discomfort in the chest.
4.Hemorrhoids:
Swollen Veins: Enlarged veins inside and outside the anus and rectum.
Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, and rectal bleeding.
5.Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis):
Viral Infection: Infection of the stomach and upper part of the small intestine.
Duration: Typically lasts less than a week.
6.Ulcers:
Sore Development: Sores on the lining of the esophagus, stomach, or small intestine.
Causes: Helicobacter pylori infection and prolonged use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
7.Gallstones:
Solid Material Formation: Small pieces formed from digestive fluid in the gallbladder.
Chronic Diseases:
GERD (Chronic Acid Reflux):
Frequent Acid Backflow: Acid-containing contents in the stomach frequently leak into the esophagus.
Symptoms: Persistent heartburn and regurgitation.
2,Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Colon Muscle Dysfunction: Irregular contractions leading to excessive gas, abdominal pain, and cramps.
Chronic Nature: A long-term condition affecting bowel function.
3.Lactose Intolerance:
Inability to Digest Lactose: Results in digestive discomfort after consuming milk and dairy products.
Common Symptoms: Bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
4.Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis:
Colon Pockets Formation: Diverticula (pockets) in the wall of the colon.
Complications: Inflammation (diverticulitis) can occur, causing pain and infection.
5.Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers:
Tissue and Organ Affliction: Cancers affecting the digestive system, including esophageal, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers.
6.Crohn’s Disease:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A lifelong condition causing inflammation in the digestive tract.
7.Celiac Disease:
Autoimmune Disorder: Gluten consumption damages the small intestine.
Trigger: Found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Care Practices for Digestive Health

Maintaining a healthy digestive system involves adopting proactive lifestyle and dietary habits:
1.Hydration:
Importance of Water: Drinking water facilitates smooth food flow, preventing dehydration-related constipation.
Dehydration Consequences: Insufficient water intake can lead to dry and hard stool.
2.Fiber-Rich Diet:
Benefits of Fiber: Supports digestion and regular bowel movements.
Soluble and Insoluble Fiber: Both types contribute to digestive health.
3.Balanced Nutrition:
Fruits and Vegetables: Multiple servings daily for essential vitamins and minerals.
Whole Grains: Choosing whole grains over processed grains.
Limiting Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
4.Probiotics:
Role of Probiotics: Supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Post-Antibiotic Use: Especially beneficial after antibiotic treatments.
5.Mindful Eating:
Chewing and Digestion: Thorough chewing aids in proper digestion.
Eating Pace: Slower eating allows the body to signal fullness.
6.Physical Activity:
Exercise and Digestion: Physical activity and gravity aid in moving food through the digestive system.
Post-Meal Walks: Taking a walk after meals can enhance digestion.
7.Avoiding Harmful Habits:
Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake to prevent acid-related issues.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves digestive symptoms.
8.Stress Management:
Stress and Digestive Issues: Association between stress and conditions like constipation, diarrhea, and IBS.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating stress-relief practices into daily life.
Seeking Medical Attention
While occasional digestive issues are common, persistent symptoms warrant attention:
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider:
Frequent Symptoms: Constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, excessive gas, or heartburn.
Potential Underlying Issues: Frequent occurrences may indicate a more serious digestive system problem.
2.Importance of Medical Evaluation:
Diagnostic Assessment: Identifying the cause of persistent symptoms.
Early Intervention: Timely treatment prevents potential complications.
3.Collaborative Approach:
Healthcare Professional Guidance: Seeking advice on managing and preventing digestive issues.
Individualized Care: Tailoring interventions based on the individual’s health status and conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the details of the digestive system provides a foundation for promoting digestive health. The collaboration of organs in the GI tract and the biliary system highlights the complexity of the digestive process. Awareness of common conditions, care practices, and the significance of seeking medical attention empowers individuals to prioritize their digestive well-being. Adopting a holistic approach that combines a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and regular medical check-ups ensures a resilient and well-functioning digestive system, contributing to overall health and vitality.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
Interesting Nursing Topics To Choose For A Case Study

Childhood Nursing
Antibiotics Impact on Childhood Immunities
Antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine, significantly improving the prognosis for many infectious diseases. However, the impact of antibiotics on childhood immunities is a multifaceted topic that warrants careful examination. While antibiotics target harmful bacteria, they may also affect the delicate balance of the immune system in developing children.
Research could delve into the long-term consequences of antibiotic use during childhood, exploring how it may influence the development of the immune system. Are there specific types of antibiotics that pose greater risks? What role do probiotics play in mitigating the potential negative effects of antibiotics on the immune system? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing pediatric care and ensuring the long-term health of children.
Effects of Childhood Exposure to Environmental Pollutants

Children are particularly vulnerable to environmental pollutants, and exposure during early life stages can have lasting health implications. Research in this area could focus on specific pollutants, such as air pollutants, heavy metals, or endocrine disruptors, and their impact on children’s health.
Exploring the effects of second-hand smoke inhalation during early life stages is particularly relevant. What are the respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of childhood exposure to second-hand smoke? How does environmental pollution contribute to respiratory conditions in children, and what preventive measures can be implemented?
Ethics of Pediatric Care
The ethical dimensions of pediatric care are intricate, involving considerations of autonomy, beneficence, and justice. Topics within this realm could include ethical dilemmas faced by pediatric nurses, such as decision-making in cases where parental and child interests may conflict.
Research may also explore the ethical implications of emerging technologies in pediatric care. For instance, what are the ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing in children? How can nurses navigate the ethical challenges posed by advances in pediatric treatments and interventions?
Genetic Factors of Diabetes in Children

The increasing prevalence of diabetes in children raises questions about the genetic factors contributing to this trend. Research in this area could delve into the genetic markers associated with pediatric diabetes, exploring the hereditary aspects of the disease.
Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial. What role do lifestyle factors play in the manifestation of diabetes in genetically predisposed children? How can nurses incorporate genetic counseling into pediatric diabetes management to empower families with the knowledge needed for preventive strategies?
How Health in Children Can Affect Their Health Later in Life
The concept that early life experiences can shape health outcomes in adulthood is a key area of interest. Research could investigate the link between childhood health and long-term health trajectories. Are there specific childhood health indicators that serve as predictors of adult health issues?
Exploring the mechanisms through which childhood health influences adulthood health can guide nursing interventions. How can nurses promote healthy behaviors in children that have lasting effects on their well-being? What preventive measures can be implemented during childhood to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood?
Adult Nursing
Analyzing the Benefits of Collaborative Nursing
Collaborative nursing involves interdisciplinary teamwork to enhance patient care outcomes. Research in this area could explore the benefits of collaborative nursing practices in diverse healthcare settings. What are the positive outcomes associated with collaborative care, such as improved patient satisfaction, reduced hospital readmissions, or enhanced treatment adherence?
Understanding the factors that contribute to successful collaboration is essential. How do effective communication and shared decision-making impact collaborative nursing efforts? What challenges do nurses face in interprofessional collaboration, and how can these challenges be addressed to optimize patient care?
Analyzing the Causes of Depression

Depression is a prevalent mental health concern affecting a significant portion of the adult population. Research into the causes of depression can provide valuable insights into preventive measures and targeted interventions. This could involve exploring the interplay between genetic, environmental, and psychological factors in the development of depression.
Investigating the role of adverse childhood experiences in predisposing individuals to depression in adulthood is a pertinent avenue. How can nurses identify individuals at risk based on early life experiences? What interventions can be implemented to break the cycle of depression rooted in childhood trauma?
Ethics of Data Collection in Adult Health Care
The ethical considerations surrounding data collection in adult health care are paramount, especially in the era of electronic health records and data-driven healthcare. Research could delve into the ethical challenges nurses face in collecting, storing, and utilizing patient data.
Exploring the perspectives of patients regarding data privacy and consent is crucial. How do patients perceive the use of their health data for research purposes? What safeguards can be implemented to ensure ethical data practices in adult health care settings?
Evolution of Nursing in a Specific Time Period
The evolution of nursing over time reflects changes in healthcare practices, societal attitudes, and technological advancements. Research in this area could focus on a specific time period, examining how nursing roles, responsibilities, and education have transformed.
For example, a study could explore the evolution of nursing during a period of significant healthcare reform. What were the key drivers of change, and how did nurses adapt to new models of care? Understanding historical contexts can inform current nursing practices and guide future developments in the profession.
Nonchemical Treatments for Bipolar Disorders

Bipolar disorders present unique challenges in terms of management and treatment. Research into nonchemical treatments for bipolar disorders can provide valuable alternatives or complementary approaches to medication-based interventions.
Exploring the efficacy of psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications in managing bipolar disorders is essential. How can nurses incorporate nonchemical treatments into holistic care plans for individuals with bipolar disorders? What role does patient education play in promoting self-management strategies for bipolar conditions?
Midwifery Nursing
Analysis of Caseload and Quality of Care for Underrepresented Groups
Midwives play a crucial role in maternal and infant care, yet disparities in care outcomes persist among underrepresented groups. Research in this area could investigate the caseloads and quality of care provided to women from marginalized communities.
Examining the experiences of midwives in catering to diverse caseloads can provide insights into challenges and opportunities. How do midwives adapt their care approaches to address the unique needs of underrepresented populations? What strategies can be implemented to ensure equitable access to high-quality midwifery care?
Analysis of Childbirth Experiences of Women with Autism

Pregnancy and childbirth can pose unique challenges for women with autism spectrum disorders. Research could explore the childbirth experiences of women with autism, considering factors such as sensory sensitivities, communication preferences, and support needs.
Understanding the specific needs of this population can inform midwifery practices and improve the overall childbirth experience. What adjustments can be made in maternity care settings to accommodate the needs of women with autism? How can midwives collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care for pregnant individuals with autism?
Nonchemical Pain Management in Labor
Labor pain is a central aspect of childbirth, and nonchemical pain management approaches are gaining attention. Research in this area could focus on the effectiveness of non-pharmacological pain management methods during labor.
Exploring techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, acupuncture, and mindfulness can provide valuable insights. How do these nonchemical methods influence pain perception and labor outcomes? What role can midwives play in promoting and facilitating the use of non-pharmacological pain management strategies during childbirth?
Role of Midwifery in Emergency Care
While childbirth is often a natural process, emergencies can arise, requiring swift and effective interventions. Research could investigate the role of midwives in emergency care.
Conclusion
In this expansive discussion, we have explored a variety of nursing research topics across different specializations. Each topic presents unique challenges, opportunities, and areas for further exploration within the field of nursing. Whether focusing on pediatric care, mental health, women’s health, or health care management, the diverse range of topics reflects the major areas to consider.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.
What Are The Stages of Fetal Growth During Pregnancy?

The development of a fetus during pregnancy is a complex and remarkable process, marked by significant changes and growth each month. This journey is typically divided into three stages known as trimesters, each lasting approximately three months. For Healthcare professionals we discuss fetal development in terms of weeks. Here’s a detailed overview of what entails during each month of pregnancy.
a) First Trimester

The first trimester of pregnancy encompasses weeks 1 through 12 and is characterized by the initial formation and rapid development of the embryo. This period is critical for establishing the foundation of the future baby’s organs and body systems. The first trimester is often associated with the onset of pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea, fatigue, and hormonal changes.
Month 1 (Weeks 1–4)
Weeks 1–2: The first two weeks of pregnancy are technically considered a preparatory period. During this time, the body releases hormones and prepares the uterus for a potential pregnancy. This period includes ovulation, where an egg is released from the ovary. If fertilization occurs, the zygote forms and marks the beginning of pregnancy.
Week 3: Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell meets the egg, creating a zygote. This single-celled entity undergoes rapid cell division as it travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
Week 4: The zygote becomes a blastocyst, which is a cluster of cells that implants itself into the uterine lining. The amniotic sac and placenta begin to form, playing crucial roles in protecting and nourishing the developing embryo. By the end of this month, the blastocyst is about 2 millimeters long, roughly the size of a poppy seed.
Month 2 (Weeks 5–8)
The second month of pregnancy marks significant developmental milestones as the embryo transitions into more complex forms.
Week 5: The neural tube, which will become the brain and spinal cord, begins to form. The heart, initially a simple tube, starts to pulse, setting the stage for the development of the circulatory system.
Week 6: Limb buds appear, which will eventually become arms and legs. Structures for the ears, eyes, and mouth start to take shape. Blood cells begin to form, and circulation starts within the embryo.
Week 7: The process of ossification starts as bones begin replacing the soft cartilage, and the formation of the genitals commences. The embryo now resembles a tadpole due to its prominent tail.
Week 8: Major organs and body systems continue to develop. The hands and feet start to form web-like structures, and the umbilical cord, which provides nutrients and oxygen to the embryo, is fully developed. By the end of this month, the embryo, now referred to as a fetus, is about 0.5 to 1 inch long, similar to a black bean.
Month 3 (Weeks 9–12)
The third month of pregnancy is marked by significant growth and maturation of the embryo, transitioning into a more recognizable human form.
Week 9: Teeth and taste buds begin to form. The fetus starts developing muscles, and its body takes on a more human appearance, although the head remains disproportionately large.
Week 10: Limbs and digits are fully formed, and the external genitals start to develop, although they are not yet visible on an ultrasound. The placenta continues to grow, providing essential nutrients to the fetus.
Week 11: The fetus begins to move spontaneously, exploring its surroundings by opening and closing its fists and mouth. The bones harden, though the skin remains translucent. Facial features such as the nose and lips become more defined.
Week 12: All essential organs, limbs, bones, and muscles are present and will continue to mature and develop. The fetus is about 2.5 to 3 inches long, roughly the size of a plum. At this stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases significantly, and many women begin to feel relief from early pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness.
Second Trimester

The second trimester of pregnancy spans from weeks 13 to 26. This period is often considered the most comfortable phase of pregnancy as many early symptoms subside, and the risk of miscarriage decreases. The fetus undergoes significant growth and development, and the mother begins to feel fetal movements, known as quickening.
Month 4 (Weeks 13–16)
During the fourth month, the fetus continues to develop rapidly, and its features become more distinct.
Week 13: Vocal cords form, and the fetus’s head starts to grow proportionally to the rest of the body. The fetus begins to practice breathing movements by inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid, which helps develop the lungs.
Week 14: The skin starts to thicken and fine hair, known as lanugo, begins to grow. The fetus can bring its fingers to its mouth and may start sucking its thumb. External genitals are fully formed, and fingerprints start to develop.
Week 15: The intestines and ears move to their final positions. The fetus practices more purposeful movements, such as thumb-sucking and smiling. The developing nervous system allows the fetus to respond to external stimuli, such as light and sound.
Week 16: The fetus can hear and respond to external sounds. Its eyes, although still closed, can perceive light. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 5 inches long and weighs around 4 ounces, comparable to an avocado.
Month 5 (Weeks 17–20)
The fifth month of pregnancy is marked by increased fetal activity and continued growth.
Week 17: Fat begins to accumulate under the skin, providing insulation and energy reserves. The fetus’s skin is covered with a protective coating called vernix, which prevents it from becoming chapped by the amniotic fluid.
Week 18: The fetus is covered in lanugo, which helps keep it warm and provides an additional layer of protection. The fetus starts to establish a sleep-wake cycle, and its movements become more noticeable to the mother.
Week 19: The fetus’s movements, including kicks and punches, become more frequent and noticeable. Unique fingerprints are fully formed, and the fetus may start to experience hiccups.
Week 20: Nails develop fully, and the sensory areas of the brain mature, allowing the fetus to respond more actively to its environment. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 9 to 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound.
Month 6 (Weeks 21–24)
The sixth month of pregnancy is a period of significant development, particularly in the nervous and respiratory systems.
Week 21: Coordinated limb movements become more frequent, and the fetus’s bone marrow begins producing blood cells.
Week 22: The fetus’s grasping reflex strengthens, and it can touch its surroundings, including its own body and the umbilical cord. It can hear internal sounds, such as the mother’s heartbeat and external sounds, such as voices and music.
Week 23: The fetus’s viability outside the womb increases, though intensive medical care would be necessary if it were born prematurely. The fetus starts rapidly accumulating fat, which is essential for temperature regulation after birth.
Week 24: Lung development progresses, although the lungs are not yet mature enough for the fetus to breathe independently. The fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs around 2 pounds.
Third Trimester

The third trimester of pregnancy spans from weeks 27 to 40 and is characterized by rapid growth and final preparations for birth. During this period, the fetus gains weight quickly and undergoes the final stages of development necessary for survival outside the womb.
Month 7 (Weeks 25–28)
During the seventh month, the fetus continues to grow and develop reserves of body fat.
Week 25: Increased body fat makes the fetus’s skin less wrinkled and more plump. The nervous system matures rapidly, enhancing the fetus’s ability to respond to stimuli.
Week 26: Melanin production begins, contributing to the skin and eye color. The lungs start producing surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs function properly after birth.
Week 27: The fetus’s eyes open, and it develops eyelashes. The fetus begins to develop regular sleep and wake patterns, and its movements become more coordinated.
Week 28: The fetus may begin to position itself head-down in preparation for birth. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 14 to 15 inches long and weighs between 2 to 3 pounds.
Month 8 (Weeks 29–32)
The eighth month of pregnancy involves continued maturation and growth of the fetus, with a focus on brain development.
Week 29: The fetus’s movements become more distinct as space in the uterus becomes cramped. The brain develops rapidly, allowing the fetus to control its body temperature more effectively.
Week 30: The fetus’s brain continues to grow, and it can process information and respond to stimuli. The fetus begins to establish more distinct patterns of activity and rest.
Week 31: The fetus’s skin loses its translucency as fat accumulates beneath it. Most organs, except for the brain and lungs, are fully developed and ready for birth.
Week 32: The fetus is about 17 to 18 inches long and weighs up to 5 pounds. The brain continues to develop rapidly, and the fetus can hear and respond to a variety of sounds.
Month 9 (Weeks 33–36)
During the ninth month, the fetus continues to grow and mature, preparing for birth.
Week 33: The fetus’s bones harden, although the skull remains soft and flexible to facilitate passage through the birth canal.
Week 34: The protective vernix coating thickens, providing additional protection to the fetus’s skin.
Week 35: Brain growth continues, and the fetus’s brain is now capable of regulating essential body functions.
Week 36: The lanugo covering the fetus’s body begins to disappear, and hair growth occurs on the head. The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs 6 to 7 pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37–40)
The final month of pregnancy is a period of final preparations for birth, with the fetus reaching full maturity.
Week 37: The fetus’s toenails reach the tips of its toes. It continues to gain weight rapidly, preparing for the energy demands of life outside the womb.
Week 38: The fetus’s weight gain continues, and it starts to shed the vernix coating. The fetus moves lower into the pelvis in preparation for birth.
Week 39: The fetus is considered full-term and continues to develop and gain weight. It measures about 18 to 20 inches long and weighs between 7 to 9 pounds.
Week 40: The fetus is ready for birth. Its organs are fully developed and capable of functioning independently. The fetus positions itself head-down in the pelvis, preparing for delivery.
Throughout pregnancy, the fetus undergoes substantial growth and development, preparing for the transition to life outside the womb. Regular monitoring and care by healthcare providers are crucial to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. This comprehensive journey from a single cell to a fully developed baby highlights the incredible complexity of human development.
Expert Academic Assignment Help specializes in supporting medical students to study fetal growth during pregnancy. Our assistance includes study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation, ensuring students understand fetal development. We provide mentorship, empowering students to excel academically and become competent healthcare professionals. Email: expertassignment46@gmail.comac
14 Common Lung Diseases

Introduction
Lung diseases represent some of the most severe health threats globally. The rise of industrialization, environmental pollution, and tobacco usage significantly contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. This article, outlines the most common lung diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Pneumonia

Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It poses a significant risk to the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with chronic conditions but can also affect healthy individuals. Pneumonia can be classified based on the causative agent, such as bacterial pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), viral pneumonia (e.g., influenza virus), or fungal pneumonia (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii).
Symptoms
Fever
Cough with sputum
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Sweating and shaking chills
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (less common)
Diagnosis Diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify the causative agent.
Treatment Depending on the cause, treatments may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Antifungal therapies for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and manage pain can also alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation.
2. Bronchitis

Bronchitis involves the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be acute, often following colds or the flu, or chronic, usually resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like pollution or dust.
Symptoms
Persistent cough (productive or dry)
Sputum production (clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green)
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Slight fever and chills
Chest discomfort
Diagnosis Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope. Additional tests, such as a chest X-ray, sputum tests, or pulmonary function tests, may be conducted to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or asthma.
Treatment
Acute bronchitis: Symptomatic treatment includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough medications. Inhalers or nebulizers may be prescribed to ease breathing.
Chronic bronchitis: Management may involve bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are crucial for treatment.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

COPD is a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, primarily due to smoking, environmental pollutants, or long-term exposure to respiratory irritants. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, conditions that often coexist and lead to airflow obstruction.
Symptoms
Chronic cough
Sputum production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Frequent respiratory infections
Fatigue
Unintended weight loss (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis COPD is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical examination, and spirometry, a test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis may also be used.
Prevention and Treatment Preventive measures include:
Smoking cessation
Vaccinations (influenza and pneumococcal vaccines)
Reducing exposure to lung irritants
Treatments involves;
Bronchodilators to relax the muscles around the airways
Inhaled steroids to reduce airway inflammation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Surgery (e.g., lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant) in advanced cases
4. Lung Cancer

Lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lung tissues. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, radon), and genetic predisposition.
Types
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Often linked to heavy smoking, SCLC is aggressive and spreads quickly.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): More common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Chest pain
Weight loss
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Shortness of breath
Hoarseness
Bone pain (in advanced stages)
Headache (if cancer spreads to the brain)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves imaging tests (chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), sputum cytology, and tissue biopsy. Molecular testing may be done to identify specific genetic mutations that can be targeted with specific treatments.
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the lung
Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors
Targeted drug therapies to attack specific genetic changes in cancer cells
Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is the inflammation of the pleura, the tissue lining the lungs and chest cavity. It can be caused by infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), injuries, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms
Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Shortness of breath
Cough
Fever (if infection is present)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause. Thoracentesis, a procedure to remove and analyze pleural fluid, may be performed.
Treatment Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections
Antiviral medications for viral infections
Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Pain management with medications
Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from the pleural space
6. Pulmonary Embolism

A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot, usually originating in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow and causing tissue damage. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, and certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms
Sudden shortness of breath
Chest pain (may be sharp and worsen with deep breathing or coughing)
Cough (sometimes with bloody sputum)
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Lightheadedness or dizziness
Leg pain or swelling (if DVT is present)
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT pulmonary angiography, and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans. D-dimer blood tests and ultrasound of the legs may also be conducted.
Treatment Immediate treatment includes:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting
Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving medications) for severe cases
Surgical or catheter-based procedures to remove the clot
Long-term anticoagulation therapy to prevent recurrence
7. Pulmonary Edema

Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lung alveoli, making breathing difficult. It can result from heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or exposure to high altitudes (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
Symptoms
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea), especially when lying down
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Wheezing or gasping for breath
Coughing up frothy, pink-tinged sputum
Excessive sweating
Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Echocardiography and pulmonary artery catheterization may be used to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treatment Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include:
Diuretics to remove excess fluid
Medications to improve heart function (for cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation
Treating underlying conditions such as infections or high altitude exposure
8. Pulmonary Fibrosis

Pulmonary fibrosis is the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to reduced oxygen absorption. Causes include chronic exposure to environmental pollutants, infections, genetic factors, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., scleroderma).
Symptoms
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Persistent dry cough
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Aching muscles and joints
Clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingertips or toes
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, imaging tests (chest X-rays, high-resolution CT scans), pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsy. Blood tests may be used to identify underlying autoimmune diseases.
Treatment While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments focus on symptom management and slowing progression:
Medications such as pirfenidone and nintedanib to slow disease progression
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung transplant in severe cases
9. Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling dust particles, such as asbestos, silica, or coal dust, leading to lung scarring. It is a type of occupational lung disease commonly seen in miners, construction workers, and industrial workers.
Symptoms:
Chronic cough
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Progressive loss of lung function
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed occupational history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess the extent of lung damage.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Avoiding further exposure to dust
Medications to manage symptoms, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Respiratory therapies
Pulmonary rehabilitation
10. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
PAH is a form of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. It can be idiopathic, familial, or associated with other conditions such as connective tissue diseases, congenital heart disease, or chronic liver disease.
Symptoms
Breathing difficulties (dyspnea), especially during physical activities
Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
Chest pain
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen (edema)
Cyanosis (bluish lips and skin)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves echocardiography, right heart catheterization, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung and heart function.
Treatment Treatment strategies include:
Medications to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, such as endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, and prostacyclin analogs
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
Oxygen therapy
Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as atrial septostomy or lung transplant
11. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs. This results in frequent infections, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Persistent cough with thick mucus
Recurrent lung infections
Wheezing or shortness of breath
Poor growth and weight gain in children
Salty-tasting skin
Severe constipation
Frequent greasy, bulky stools
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat chloride tests, and newborn screening. Pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures may also be conducted to assess lung health.
Treatment Management includes:
Medications to thin mucus, antibiotics to treat infections, and bronchodilators to open airways
Chest physiotherapy to clear mucus
Enzyme supplements and high-calorie diets to manage digestive issues
Newer therapies targeting the underlying genetic defect, such as CFTR modulators
12. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS primarily affects premature infants due to a lack of surfactant, a substance necessary to keep the lungs open and facilitate gas exchange. Risk factors include premature birth, maternal diabetes, and multiple births.
Symptoms
Rapid, shallow breathing
Grunting sounds while breathing
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles)
Cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, chest X-rays, and blood gas analysis to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Prenatal tests can also help identify at-risk pregnancies.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Surfactant replacement therapy to improve lung function
Mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) to support breathing
Oxygen therapy
Supportive care such as fluids and nutrition
13. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of granulomas (small clusters of inflammatory cells) in the lungs and other organs, likely as an immune response to unknown triggers. The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms
Dry cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Skin lesions (e.g., erythema nodosum)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. Biopsy of affected tissues may be performed to confirm the presence of granulomas.
Treatment While sarcoidosis is often self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, severe cases may require:
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., methotrexate, azathioprine)
Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) for skin lesions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage chronic cases
14. Asthma
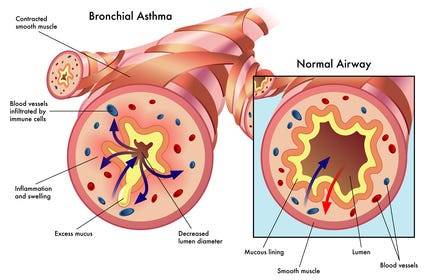
Definition and Causes: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, causing episodes of wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Symptoms
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Increased mucus production
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests (spirometry, peak flow measurement). Allergy testing and chest X-rays may also be conducted to identify triggers and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Management includes:
Avoiding known triggers
Inhalers (bronchodilators for quick relief, corticosteroids for long-term control)
Long-term control medications (e.g., leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists)
Immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe allergies
Asthma action plans to manage symptoms and prevent attacks
Conclusion
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Preventive measures such as avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and timely vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing many of these diseases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by lung diseases. For personalized medical advice and treatment, consult with healthcare professionals.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.
What Are The Routes Of Drug Administration?

The administration of drugs is a fundamental aspect of medical treatment, influencing the efficacy, onset, and duration of therapeutic effects. Understanding the various routes of drug administration is crucial for healthcare professionals to optimize patient outcomes and minimize adverse effects. Each route has distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting factors such as absorption, bioavailability, patient compliance, and suitability for different clinical scenarios.
1. Oral Route
The oral route involves administering the drug via the mouth, allowing it to be absorbed into the systemic circulation through the gastrointestinal tract. It is the most frequently used route for drug administration due to its simplicity and non-invasive nature.
Dosage Form
Solid: Tablets (including immediate-release, enteric-coated, and modified-release forms), capsules, granules, powders.
Liquid: Syrups, elixirs, suspensions.
Advantages
Cost-effective: The oral route is generally less expensive compared to other routes of administration.
Safe and non-invasive: It is a relatively safe method and does not involve any invasive procedures.
Simple and convenient: Patients can easily take oral medications without requiring special skills or tools.
Self-administration: Patients can manage their medication intake independently, enhancing compliance.
Disadvantages
Variable absorption: Drug absorption can be influenced by several gastrointestinal factors such as motility, gastric emptying rate, and the presence of food.
First-pass metabolism: Drugs administered orally are subject to first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can reduce the bioavailability of the active drug.
Unsuitable for certain patients: This route is not ideal for unconscious or vomiting patients.
Slow onset of action: Oral medications typically have a slower onset of action compared to other routes.
Potential degradation: Some drugs may be degraded by digestive enzymes or stomach acid, reducing their effectiveness.
2. Sublingual Route
The sublingual route involves placing the drug under the tongue, where it is absorbed through blood vessels directly into the systemic circulation, thereby bypassing first-pass metabolism. This method is particularly useful for drugs that require rapid onset of action.
Dosage Forms
Tablets (e.g., glyceryl trinitrate)
Films (e.g., suboxone)
Sprays (e.g., glyceryl trinitrate)
Advantages
Rapid absorption and onset of action: Drugs administered sublingually are quickly absorbed, providing fast relief.
Avoids first-pass metabolism: This enhances the bioavailability of the drug.
Self-administration: Patients can easily administer the medication themselves.
Quick termination of action: The effect can be quickly terminated by spitting out the sublingual tablet if necessary.
Disadvantages
Limited availability: Not all drugs are available in sublingual formulations.
Unpleasant taste: Some sublingual drugs may have a bitter or unpleasant taste.
Potential inconvenience: Holding the drug under the tongue until it dissolves can be inconvenient for some patients.
Mucosal irritation: There is a risk of irritation to the oral mucosa.
3. Buccal Route

The buccal route involves placing the drug between the gum and the inner cheek. This allows for rapid absorption through the buccal mucosa into the systemic circulation, bypassing first-pass metabolism.
Dosage Forms
Tablets (e.g., prochlorperazine maleate)
Chewing gum (e.g., nicotine gum)
Advantages
Rapid absorption: The drug is quickly absorbed through the buccal mucosa.
Avoids first-pass metabolism: This enhances the drug’s bioavailability.
Convenient for patients: It provides a convenient method of drug administration.
Disadvantages
Unpleasant taste: Some buccal medications may have an unfavorable taste.
Potential mucosal irritation: There is a risk of irritation to the buccal mucosa.
4. Intravenous (IV) Route

The intravenous route involves administering the drug directly into a vein, providing immediate effects. This route is often used in emergency situations where rapid drug action is necessary.
Dosage Forms
Injections
Emulsion injections
Solutions for injection and infusion
Advantages
Immediate effect: Drugs administered intravenously provide immediate therapeutic effects, making this route ideal for emergencies.
Suitable for unconscious patients: It can be used in patients who are unconscious or unable to swallow.
Predictable and precise control: IV administration allows for precise control over drug plasma levels.
Disadvantages
Risk of anaphylaxis and infection: There is a potential for severe allergic reactions and infections.
Inconvenient and painful: IV administration can be uncomfortable and requires skilled personnel.
Higher cost: It is generally more expensive compared to other routes.
Irreversibility: Once administered, the drug cannot be recalled, which can be a significant disadvantage if adverse effects occur.
5. Intramuscular (IM) Route

The intramuscular route involves injecting the drug directly into a muscle, typically the gluteus medius or deltoid. This method allows for slower, more sustained absorption compared to intravenous administration.
Dosage Forms
Solutions for intramuscular injection
Advantages
Immediate onset: The drug begins to act relatively quickly.
Depot or sustained release: Some formulations are designed for slow, sustained release.
Avoids first-pass metabolism: This route bypasses hepatic first-pass metabolism.
Easier than IV administration: IM injections are generally easier to administer than IV infusions.
Disadvantages
Higher cost: Intramuscular injections are often more expensive than oral medications.
Painful and variable absorption: Injections can be painful, and absorption can vary based on the muscle group and blood flow.
Requires trained personnel: Administration typically requires a healthcare professional.
6. Subcutaneous (SC) Route

The subcutaneous route involves injecting the drug into the subcutaneous tissue, either as a direct injection or infusion. This method allows for slower absorption compared to intramuscular injections.
Advantages
Suitable for self-administration: Patients can often administer subcutaneous injections themselves.
Long duration of action: Some drugs have a prolonged effect when administered subcutaneously.
Low risk of systemic infection: The risk of infection is generally lower compared to intravenous administration.
Disadvantages
Variable absorption: Drug absorption can vary based on blood flow to the injection site.
Limited to small drug volumes: Only small volumes of medication can be administered subcutaneously.
7. Inhalation Route
Description: The inhalation route involves inhaling the drug, which is delivered to the lungs for either local or systemic effects. This method is commonly used for respiratory conditions.
Dosage Forms
Metered-dose inhalers (MDIs)
Dry powder inhalers
Advantages
Rapid onset: Inhaled drugs provide quick relief, especially for respiratory conditions.
Minimizes systemic side effects: The drug is delivered directly to the site of action, reducing systemic exposure.
Targets the site of action: This route is effective for treating conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Disadvantages
Requires proper technique: Effective drug delivery depends on the patient’s ability to use the inhaler correctly.
Limited to a few drugs: Not all medications can be administered via inhalation.
Potential for cough reflex stimulation: Inhaled drugs can sometimes trigger coughing.
8. Nasal Route
The nasal route involves administering the drug directly into the nose, where it is absorbed through the nasal mucosa into systemic circulation or used for localized effects.
Dosage Forms
Nose sprays
Nose drops
Advantages
Rapid onset: Drugs administered nasally are quickly absorbed.
Minimal side effects: This route generally has fewer side effects compared to systemic administration.
Suitable for self-administration: Patients can easily administer nasal medications themselves.
Disadvantages
Unpleasant taste: Some nasal sprays or drops may lead to an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
9. Rectal Route
The rectal route involves administering the drug into the rectum, where it can provide localized or systemic effects.
Dosage Forms
Suppositories
Enemas
Advantages
Suitable for self-administration: Patients can manage rectal medications independently.
Reduced first-pass metabolism: This route reduces the extent of hepatic first-pass metabolism.
Useful for specific patient populations: It is beneficial for patients who are unconscious, vomiting, or unable to swallow.
Disadvantages
Uncomfortable and messy: This route can be unpleasant and inconvenient for patients.
Variable absorption: Drug absorption can be inconsistent.
Low patient acceptance: Many patients are reluctant to use rectal medications.
10. Vaginal Route
The vaginal route involves administering the drug into the vagina, typically for localized effects but sometimes for systemic absorption.
Dosage Forms
Pessaries
Creams
Rings
Advantages
Suitable for self-administration: Patients can administer vaginal medications independently.
Avoids first-pass metabolism: This route bypasses hepatic first-pass metabolism.
Effective for localized conditions: It is particularly useful for treating vaginal infections or conditions.
Disadvantages
Uncomfortable and messy: Vaginal administration can be unpleasant and inconvenient.
Compliance issues: There may be challenges with patient adherence.
Potential irritation: Some formulations can cause local irritation.
11. Cutaneous Route
The cutaneous route involves applying the drug to the skin for localized effects, commonly used in dermatological treatments.
Dosage Forms
Ointments
Creams
Powders
Solutions
Shampoos
Advantages
Self-administration: Patients can easily apply cutaneous medications themselves.
Avoids systemic side effects: Localized application minimizes systemic drug interactions and side effects.
Disadvantages
Messy and time-consuming: Some preparations can be difficult to apply and may be messy.
Potential for adverse reactions: There is a risk of adverse reactions to the excipients in the dosage form.
12. Otic (Ear) Route
The otic route involves administering the drug to the ear, typically for treating local ear conditions.
Dosage Forms
Ear drops
Advantages
Effective for local treatment: This route is effective for treating ear infections and other local conditions.
Disadvantages
Difficult self-administration: Some patients may find it challenging to administer ear drops themselves.
Time-consuming application: Patients often need to remain on their side or tilt their head for a few minutes after administration.
13. Ocular (Eye) Route

The ocular route involves administering the drug into the eye for treating local conditions such as infections, inflammations, or glaucoma.
Dosage Forms
Eye drops
Eye ointments
Advantages
Convenient: Eye drops and ointments are easy to administer.
Reduced systemic side effects: Local administration minimizes systemic exposure and side effects.
Disadvantages
Temporary vision blurring: Some formulations can temporarily blur vision.
Administration barriers: Patients with poor manual dexterity or vision issues may struggle with administration.
14. Transdermal Route
The transdermal route involves applying the drug to the skin, where it is absorbed into the systemic circulation. This method is often used for continuous drug delivery over an extended period.
Dosage Forms
Patches
Gels
Advantages
Convenient: Transdermal patches and gels are easy to use and require less frequent application.
Avoids first-pass metabolism: This route bypasses hepatic first-pass metabolism.
Steady plasma concentration: Provides a consistent drug release and steady plasma levels.
Long duration of action: Often suitable for long-term treatment.
Disadvantages
Expensive: Transdermal systems can be costly.
Potential for local irritation: Some patients may experience irritation at the application site.
This comprehensive overview of drug administration routes highlights the diversity of methods available for delivering medications. Each route has its unique set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the most appropriate method based on the specific therapeutic needs, patient condition, and drug characteristics.
For students seeking professional guidance on assignments, online classes, research, clinical studies, essays, and understanding medical conditions, Expert Academic Assignment Help is your trusted partner. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for expert support to navigate your academic and clinical journey with confidence and success. We are your professional partner.
The 12 Most Interesting Facts about Nursing

The nursing profession is a cornerstone of the healthcare system, rich in history, filled with unique facts, and bolstered by surprising statistics that highlight its evolution and impact. Whether you’re a registered nurse, nurse practitioner, nurse’s assistant, or involved in nurse staffing, there is always more to learn about this vital field. Here, we indulge into 12 intriguing facts about nursing that might surprise even those within the industry.
1. Nursing’s Ancient Origins

The earliest records of nursing date back to 300 A.D. in the Roman Empire, where nurses operated in what were considered hospitals at the time. These early healthcare institutions, known as valetudinaria, provided care primarily to soldiers and slaves. Nursing during this period was rudimentary and primarily focused on basic care and comfort.
The practice of nursing evolved significantly during the Middle Ages. Monastic orders, particularly in Europe, took on the role of caregivers. Monks and nuns provided care in hospices and infirmaries, laying the groundwork for modern nursing. The evolution continued with the establishment of more structured medical and nursing practices in response to the Black Death in the 14th century. These historical roots underscore the longstanding tradition of compassion and care in nursing.
2. Florence Nightingale’s Pioneering Influence

Florence Nightingale, often referred to as the founder of modern nursing, played a major role in transforming the profession. Born into a wealthy British family, Nightingale defied societal expectations to pursue a career in nursing. Her work during the Crimean War (1853–1856) brought her international acclaim. She was appalled by the unsanitary conditions and high mortality rates in military hospitals and implemented rigorous hygiene practices, significantly reducing the death rate.
Nightingale’s contributions extended beyond the battlefield. She established the Nightingale Training School for Nurses in 1860 at St. Thomas’ Hospital in London, emphasizing the importance of formal education and training for nurses. Her book, “Notes on Nursing: What It Is and What It Is Not,” became a seminal text in nursing education. Nightingale’s legacy includes her pioneering use of statistical analysis to advocate for healthcare reform, showcasing the impact of evidence-based practice.
3. The First Nursing School
The establishment of the Bellevue Hospital School of Nursing in New York City in 1873 marked a significant milestone in American nursing history. Inspired by Florence Nightingale’s principles, the school offered a one-year program that combined theoretical instruction with practical experience. This model set the standard for future nursing education.
Bellevue’s success prompted the establishment of other nursing schools, such as the New England Hospital for Women and Children (now part of the Boston Medical Center) and Massachusetts General Hospital’s nursing school. These institutions played a crucial role in professionalizing nursing and raising the standards of patient care. The emphasis on rigorous training and education helped transform nursing into a respected and essential profession.
4. The Physical Demands of Nursing
Nurses are known for their dedication and hard work, but the physical demands of the profession are often underestimated. On average, nurses walk four to five miles during a typical 12-hour shift, which is double the daily walking distance of most people. This constant movement is necessary to provide timely and effective care to patients, but it also highlights the physical challenges nurses face.
The demanding nature of nursing underscores the importance of proper footwear and ergonomics in the workplace. Comfortable, supportive shoes can help prevent injuries and reduce fatigue, enabling nurses to perform their duties effectively. Additionally, the physical activity associated with nursing contributes to overall health, but it also necessitates a focus on self-care and occupational health strategies to mitigate the risk of long-term musculoskeletal issues.
5. Dominance in Healthcare Education
Nursing is a dominant field within healthcare education, with approximately 50% of students in healthcare-related programs pursuing nursing degrees. This significant representation reflects the critical role nurses play in the healthcare system. The demand for nursing education has led to the development of numerous undergraduate and graduate programs, offering specialized training in various areas such as pediatric nursing, geriatric nursing, and critical care.
The strong support network among nursing students and professionals fosters a collaborative learning environment. Nursing programs emphasize not only clinical skills but also the development of critical thinking, communication, and leadership abilities. This comprehensive approach ensures that nursing graduates are well-prepared to meet the diverse and complex needs of patients.
6. Top Nursing Jobs
Nursing offers a wide range of career opportunities, and several nursing roles are consistently ranked among the top jobs in the United States. According to U.S. News & World Report, three nursing roles were among the top 40 jobs in 2021: registered nurses (ranked 37th), nurse anesthetists (ranked 39th), and nurse practitioners (ranked 3rd).
These rankings highlight the diverse and lucrative opportunities within the nursing profession. Registered nurses (RNs) are the backbone of healthcare, providing essential care and coordination in various settings. Nurse anesthetists, who administer anesthesia and monitor patients during surgical procedures, are highly specialized and command competitive salaries. Nurse practitioners (NPs) have advanced training that allows them to diagnose and treat medical conditions, often serving as primary care providers. The high ranking of NPs reflects the growing recognition of their critical role in expanding access to healthcare.
7. Mary Eliza Mahoney’s Legacy
Mary Eliza Mahoney, the first African American registered nurse in the United States, broke significant barriers in the field of nursing. Born in 1845 in Boston, Mahoney worked at the New England Hospital for Women and Children for 15 years before enrolling in its nursing program. She graduated in 1879, becoming one of only three graduates out of a class of 42.
Mahoney’s accomplishments extend beyond her personal achievements. She co-founded the National Association of Colored Graduate Nurses (NACGN) in 1908, advocating for the inclusion and recognition of African American nurses. The NACGN played a crucial role in supporting black nurses and promoting racial equality in the profession. Mahoney’s legacy is a testament to her resilience, dedication, and pioneering spirit, which continue to inspire nurses today.
8. The U.S. Nursing Workforce
As of 2020, there were approximately three million nurses in the United States, comparable to the population of Jamaica. This vast workforce is essential to the functioning of the healthcare system. Nurses work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, schools, and community health centers.
Globally, there are over 28 million nurses, accounting for 59% of healthcare professionals worldwide. This significant presence underscores the critical role nurses play in delivering healthcare services. However, the global nursing workforce faces challenges such as shortages, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Efforts to address these shortages include increasing educational opportunities, improving working conditions, and supporting international collaboration.
9. Projected Growth in Nursing
The nursing field is not only large but also poised for continued growth. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of registered nurses is projected to increase by 7% from 2019 to 2029. This growth is driven by several factors, including an aging population, increased prevalence of chronic diseases, and expanded access to healthcare services.
The projected growth in nursing offers substantial opportunities for those entering the profession. It also underscores the importance of supporting nursing education and training programs to meet the demand for skilled nurses. Healthcare organizations and policymakers must invest in initiatives that attract and retain nurses, ensuring a robust workforce to provide high-quality care.
10. Diverse Work Environments
While hospitals remain the largest employer of nurses, the nursing profession offers diverse work environments. According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the distribution of nurses across various settings is as follows:
Hospitals: 60%
Ambulatory healthcare services: 18%
Nursing and residential care facilities: 7%
Government: 5%
Educational services: 3%
This diversity allows nurses to work in a range of settings, each with its unique challenges and opportunities. Ambulatory healthcare services include outpatient clinics, surgical centers, and primary care practices, where nurses play a vital role in patient care and health promotion. Nursing and residential care facilities provide long-term care for individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities, emphasizing the importance of compassionate, ongoing support. Government and educational services offer roles in public health, policy, research, and academia, contributing to the advancement of the profession and the improvement of public health.
11. National Nurses Week
National Nurses Week, celebrated annually from May 6 to May 12, honors the challenging work and dedication of nurses. Established over 40 years ago, this week-long celebration culminates on May 12, the birthday of Florence Nightingale. The week recognizes the significant contributions of nurses to healthcare and society.
National Nurses Week includes various events and activities to celebrate and appreciate nurses. These may include educational seminars, award ceremonies, community outreach programs, and public awareness campaigns. The celebration provides an opportunity to highlight the vital role of nurses, advocate for their needs, and inspire the next generation of nursing professionals.
12. Staffing Agencies and Nursing Employment
Nurse staffing agencies play a crucial role in addressing the fluctuating demand for nursing services. Many nurses find employment through staffing agencies, which help them secure jobs and new opportunities. These agencies match nurses with healthcare facilities that need additional staff, ensuring that patient care remains uninterrupted.
For staffing agencies, keeping pace with the rising demand for nurses is crucial. Solutions like invoice factoring can provide the necessary funding to grow and support their operations effectively. Invoice factoring allows agencies to sell their accounts receivable at a discount in exchange for immediate cash, helping them manage cash flow and invest in recruiting and retaining qualified nurses.
Conclusion
These facts not only highlight the rich history and essential role of nursing but also underscore the profession’s ongoing evolution and the increasing opportunities within the field. Whether you’re a nurse or involved in nursing services, staying informed about these developments is key to advancing in this vital industry. The nursing profession continues to grow and adapt, driven by a commitment to providing high-quality care and improving patient outcomes.
For those involved in nurse staffing, understanding the dynamics of the nursing workforce and exploring financial solutions like invoice factoring can help meet the rising demand and ensure continued success. By recognizing the historical significance, current trends, and future prospects of nursing, we can better support and celebrate this indispensable profession.
For medical students and nurses of all categories, navigating assignments, homework, case studies, research, online classes, and challenging medical units can be daunting. Seeking professional guidance and assistance can make a significant difference in your academic and professional journey. For expert help with these challenges, consider reaching out to Expert Academic Assignment Help at expertassignment46@gmail.com Our professional support can help you excel in your studies and career.